The transferring of an organ from one species
to another is called
a. xenotransplantation.
b. transorganization.
c. illegal.
d. genomics.
e. cloning
A
You might also like to view...
In the below graph, if Bracket A represents the tidal volume and Bracket B represents the vital capacity, respectively, of a young man, what does Bracket C represent?
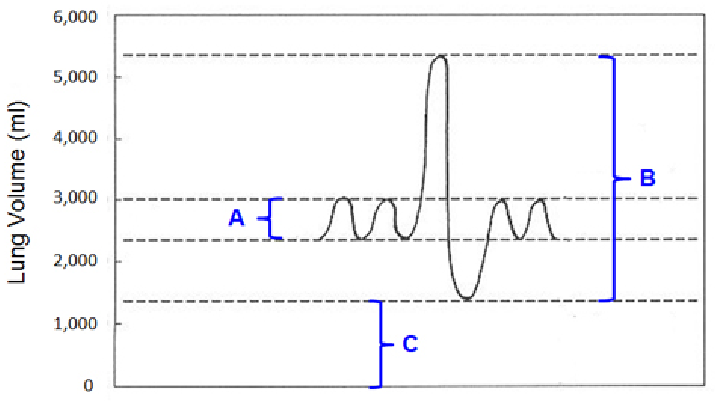
A. air that is not used for gas exchange
B. air with a concentration of oxygen higher than that of air outside the body
C. anatomical dead space
D. air from a previous breath that does not mix with newly-inhaled air of the next breath
E. air that helps keep the alveoli inflated (open) after forced exhalation
Clarify Question
What is the key concept addressed by the question?
What type of thinking is required?
Gather Content
What do you already know about the lungs? What other information is related to the question?
Choose Answer
Given what you now know, what information is most likely to produce the correct answer?
Reflect on Process
Did your problem-solving process lead you to the correct answer? If not, where did the process break down or lead you astray? How can you revise your approach to produce a more desirable result?
Meiosis in flowering plants gives rise to cells that are
a. haploid gametophytes. b. diploid sporophytes. c. sporophytes that can be haploid or diploid. d. diploid gametophytes. e. haploid sporophytes.
The northern elephant seal was hunted almost to extinction during the 18th and 19th centuries. Less than 100 seals were left to contribute to the gene pool of their future generations. Since the early 20th century, the elephant seals have been protected by law in both the U.S. and Mexico. Over 100,000 seals now inhabit the western shores of North America, all related to the small population that survived the slaughter of hunters.Scientists fear the elephant seals may be more susceptible to disease and pollution due to
A. founder effect. B. disruptive selection. C. heterozygous advantage. D. bottleneck effect.
In running an experiment, it is crucial that there exists both subjects who receive the treatment, but also subjects who do not because:
A. this allows you to run regressions in the analysis step. B. without variation in the treatment, testing the hypothesis would not be feasible. C. the treatment will be well calibrated. D. None of the answers is correct.