What accounted for much of policymakers' concern over U.S. current account deficits in the 1980s, 1990s, and 2000s?
A) The current account deficits were thought to be largely responsible for the federal budget deficit.
B) Current account deficits lower U.S. interest rates, thereby leading to reduced domestic saving.
C) Current account deficits require the United States to borrow funds from foreign savers.
D) The United States had signed international agreements in which it had pledged not to run a current account deficit for more than three years in a row.
C
You might also like to view...
The degree of control over its output price that any seller has is limited by
a. the existence of actual competition in the market. b. the existence of potential competition from producers who might try to enter the market. c. the elasticity of the demand for the product. d. All of these.
Consider two Cournot competitors selling complementary goods with demand curves given by:
p1 = 100 - q1 + .5q2 p2 = 100 - q2 + .5q1 Suppose each firm has a marginal and average cost of $10. a. What about the demand equations indicate that these goods are complements? How do they differ from the standard Cournot model? b. Find the equilibrium prices and quantities. c. Suppose the two firms merge. By doing so, the newly merged firm will act to maximize the joint profits ((q1,q2 ) = 1(q1,q2 ) + 2(q1,q2 )). Find the joint-profit maximizing price and quantities. d. Are the combined profits greater or smaller from merging? That is, is merging profitable for the firms? e. Are consumers better or worse off with the firms merging? How does this compare to the mergers of Cournot competitors selling substitutes? What does this imply about antitrust policy towards mergers of firms selling complementary goods (such as airplanes and engines, computers and processors, cars and tire companies, etc).
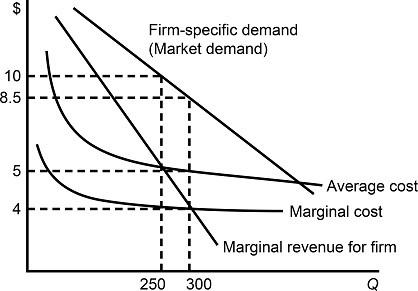 Figure 11.2Figure 11.2 shows demand and costs for a monopolistically competitive firm. At the profit maximizing output level:
Figure 11.2Figure 11.2 shows demand and costs for a monopolistically competitive firm. At the profit maximizing output level:
A. the firm is earning a positive economic profit and more firms are expected to enter the market. B. the firm is earning a zero economic profit and no firms are expected to enter the market. C. the firm is earning a negative economic profit and more firms are expected to leave the market. D. There is not sufficient information.
The city of Hope has a labor force of 1000. Twenty people lose their jobs each month and remain unemployed for exactly one month before finding jobs. On January 1, May 1, and September 1 of each year, 50 people lose their jobs for a period of four months before finding new jobs. What is the average duration of an unemployment spell?
A. 3.43 months B. 2.85 months C. 2.15 months D. 3.14 months