One of the aims of positive economics is to rank policies under consideration from most desirable to least desirable.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
False
Rationale: Positive economics aims to predict the consequences of policies, not to evaluate them as more or less desirable.
You might also like to view...
If the base year CPI basket costs $250 and next year the CPI basket costs $275, what is next year's CPI?
What will be an ideal response?
Refer to Scenario 1 . If you start the course in such a way that each exam score is worse than your previous average what should happen to your average score? What would happen to your average if the next exam score was larger than your previous exam
score? Explain.
If the money supply in the economy were at MS2, and the Federal Reserve Bank used open market operations to move money supply to MS3, the overall direct result in the economy would be: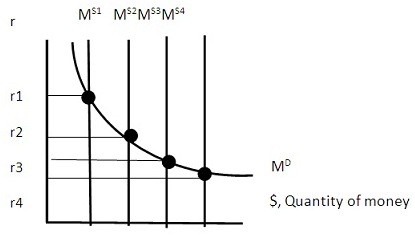
A. LRAS move to the FE level of output. B. Aggregate demand shifted in, causing GDP to fall. C. Aggregate demand shifted out, causing GDP to rise D. Aggregate supply shifted in, causing GDP to fall.
That which we forgo, or give up, when we make a choice or decision is called
A. marginal cost. B. real cost. C. opportunity cost. D. out-of-pocket cost.