The term "born with a silver spoon in his mouth" mistakenly implies
A) only monetary endowments allow one to trade with others.
B) only the wealthy are strong negotiators in trade.
C) endowments are physical.
D) endowments differ.
C
You might also like to view...
How effective is discount policy as compared to open market operations in managing the money supply? Explain how The Federal Reserve uses discount policy today
What will be an ideal response?
Assume that foreign capital flows into a nation rise due to expected increases in stock market appreciation. If the nation has highly mobile international capital markets and a fixed exchange rate system, what happens to the real risk-free interest rate and net nonreserve international borrowing/lending balance in the context of the Three-Sector-Model? a. The real risk-free interest rate falls
and net nonreserve international borrowing/lending balance becomes more positive (or less negative). b. The real risk-free interest rate falls and net nonreserve international borrowing/lending balance becomes more negative (or less positive). c. The real risk-free interest rate rises and net nonreserve international borrowing/lending balance becomes more negative (or less positive). d. The real risk-free interest rate and net nonreserve international borrowing/lending balance remain the same. e. There is not enough information to determine what happens to these two macroeconomic variables.
Assuming the inner curve is the United States' current production possibilities frontier, points J, N and K represent
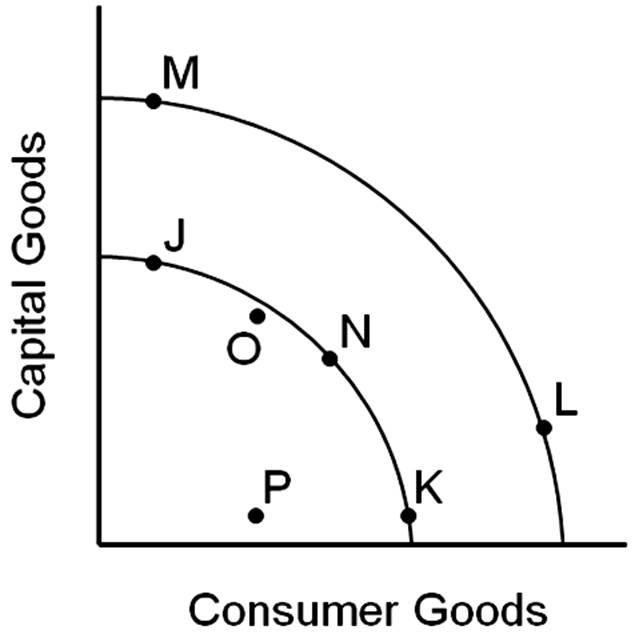
A. an inefficient use of resources.
B. an output that is not possible to produce.
C. points of unemployed resources.
D. points of fully employed resources.
The logic of collective action explains the persistence o f tariffs and quotas as an outcome that is driven by the asymmetry between
A. the benefits distributed across many consumers versus the concentration o f the costs in the hands of a few firms. B. the benefits distributed across many firms versus the concentration of the costs in the hands o f a few consumers. C . the benefit s concentrated in the hands of the few consumers, versus the costs distributed across many firms. D. the benefits concentrated in the hands of the few firms, versus the costs distributed across many consumers.