A ray of light is incident on the mid-point of a glass prism surface at an angle of 20° with the normal. For the glass, n = 1.60, and the prism apex angle is 40°. What is the angle of incidence at the glass-to-air surface on the side opposite where the ray exits the prism? The surfaces involved are those of the apex angle
a. 12.3°
c. 22.7°
b. 38.0°
d. 27.7°
D
You might also like to view...
Estimate the rotational energy (in eV) for a diatomic hydrogen molecule in the l = 2 quantum state
(The equilibrium separation for the H2 molecule is 0.074 nm.) (1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ? s, h = 1.055 × 10-34 J ? s, mH ? mproton = 1.67 × 10-27 kg) A) 0.026 eV B) 0.046 eV C) 0.055 eV D) 0.032 eV E) 0.011 eV
Why was deuterium so critical in the primordial nucleosynthesis?
What will be an ideal response?
In the context of measuring the properties of galaxies, a__________is an object of known brightness that astronomers use to find distance
A) black hole B) white dwarf C) standard candle D) red giant
A cube is 1.0 inch in length on the side (1 in = 2.540 cm). The volume of the cube is
a. 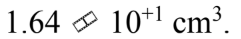
b. 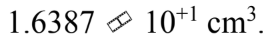
c. 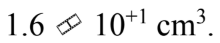
d.