Japanese employers tend to hire employees right out of college and train them for a lifetime job with the company. Over time they found that women often, but not always, married after a few years and left the company so they were not good training investments. Based on this experience, and despite the exceptions, firms stopped hiring any women for jobs that require substantial training. This
practice is called
a. economic discrimination.
b. statistical discrimination.
c. compensating differentials.
d. the substitution effect.
b
You might also like to view...
To achieve long-run equilibrium in an economy with a recessionary gap, without the use of stabilization policy, the inflation rate must:
A. not change. B. increase. C. decrease. D. either increase or decrease depending on the relative shifts of AD and AS.
Double taxation refers to
A) individuals paying taxes on wage income and individuals paying taxes on dividends. B) corporations paying taxes on capital gains and individuals paying taxes on wage income. C) corporations paying taxes on profits and individuals paying taxes on dividends. D) corporations paying taxes on profits and individuals paying taxes on wage income.
Suppose you cannot buy information that completely removes the uncertainty from a business decision that you face, but you could buy information that reduces the degree of uncertainty
Based on the discussion in this chapter, the value of this partial information could be determined as the: A) expected outcome under complete certainty minus the expected outcome under the partial information case. B) expected outcome under the partially uncertain case minus the expected outcome under the completely uncertain case. C) utility of the partially certain case minus the utility of the completely certain case. D) We cannot determine the value of information under partial certainty.
Refer to the labor market diagrams. A monopsonistic labor market is represented by Figure:
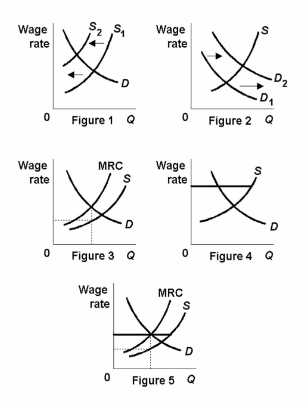
A. 5.
B. 4.
C. 3.
D. 2.