Differences in time preferences depend on
A. social preference.
B. differences in the relative size of expected future incomes.
C. the time.
D. uncertainty regarding the future.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Which of the following correctly describes a way in which deficit spending can impose a burden on future generations?
I. Failure to allocate deficit spending to uses that boost future real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) will require taxing future generations at a higher rate to repay the resulting higher public debt. II. Government deficits that lead to higher employment and real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in the future will generate increased income taxes for future governments, which will respond by spending the higher tax revenues, creating higher future government budget deficits. III. Other things being equal, deficit spending fuels increased consumption of goods and services by the current generation that crowds out capital investment, thereby leaving future generations with a smaller stock of capital than otherwise would have existed. A) I only B) II only C) I and III only D) II and III only
The income elasticity for cars is high. During the late 1960s, some U.S. citizens experienced a decrease in their real incomes. Consequently, they purchased
(a) more expensive U.S. cars. (b) more foreign imports due to their relatively low costs. (c) used U.S. cars in order to avoid foreign imports. (d) U.S. cars of any type to avoid foreign imports.
Refer to Figure 9.2. What is the Nash equilibrium of this pricing game?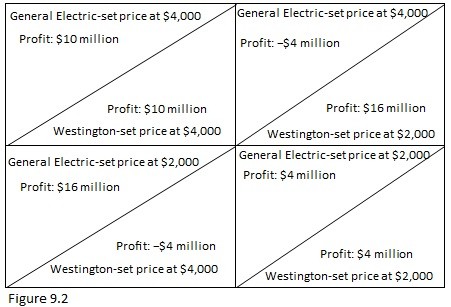
What will be an ideal response?
(Last Word) Which of the following problems has not accompanied China's rapid economic growth over the past twenty-five years?
A. High rates of inflation. B. Structural unemployment of displaced agricultural workers. C. Uneven economic development. D. Falling per capita income.