What do the three black arrows represent?
A) the tidal force Earth exerts on the Moon
B) the Moon's gravitational force at different points on Earth
C) the direction in which Earth's water is flowing
D) Earth's orbital motion
B) the Moon's gravitational force at different points on Earth
You might also like to view...
A 15 cm black disk is placed halfway between two black 3-m-diameter disks that are 7 m apart with all disk surfaces parallel to each other. If the surroundings are 0 K, determine the temperature of the two larger disks required to maintain the smaller disk at 540°C.
GIVEN
GIVEN
• A black disk (A1) halfway between two other black disks (A2 & A3)
• Diameter of A1 (D1) = 15 cm = 0.15 m
• Diameter of A2 and A3: (D2 = D3) = 3 m
• Distance between A2 and A3 (2L) = 7 m
• Surrounding temperature (T?) = 0 K
• Temperature of A1 (T1) = 540°C = 813 K
FIND
• The temperature A2 and A3 required ASSUMPTIONS
• A2 and A3 are at the same temperature (T2 = T3)
• Steady state conditions
SKETCH
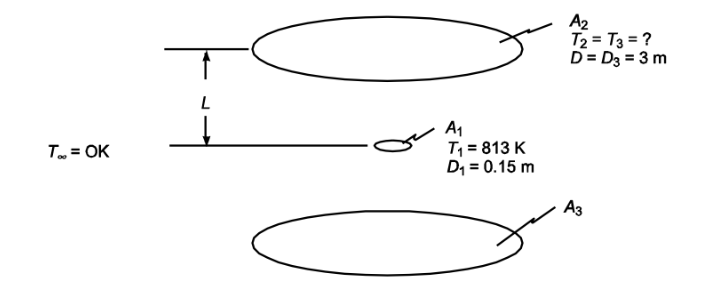
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
the Stephan-Boltzmann constant (?) = 5.67 × 10–8 W/(m2 K4)
If you observe the night sky in the direction of the North Star, you will observe that
A) the other stars near the north star move along clockwise circles around the north star during the night. B) the north star moves westward across the sky during the night. C) the other stars near the north star move in straight lines from east to west during the night. D) the other stars near the north star move along counterclockwise circles around the north star during the night. E) the north star moves eastward across the sky during the night.
A series of transitions in atomic hydrogen that produce emissions all in the ultraviolet portion of the spectrum are those ending in the level
A. n = 2. B. n = 4. C. n = 1. D. n = 3. E. n = 5.
A light ray, traveling parallel to the axis of a convex thin lens, strikes the lens near its midpoint. After traveling through the lens, this ray emerges traveling obliquely to the axis of the lens
A) such that it never crosses the axis. B) crossing the axis at a point equal to twice the focal length. C) crossing the axis at a point equal to one-half the focal length. D) passing between the lens and its focal point. E) passing through its focal point.