An example of a(n) ________ comparative advantage is U.S. consumers buying automobiles produced in Japan because Japanese companies have a reputation for producing a higher-quality automobile than those produced in the United States.
A. subsidized
B. acquired
C. natural
D. unwarranted
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
If GDP per capita in year T is represented by YT, and the GDP per capita in the following year is represented by YT+1, then the formula for calculating growth rate between these two years is ________
A) (YT+1 - YT)/YT B) (YT+1 + YT)/YT+1 C) (YT+1 + YT)/YT D) (YT+1/YT)/100
In the former Soviet Union distributing scarce consumer goods was accomplished by
A. higher prices which eliminated some potential consumers. B. making the consumer stand in a long line for hours if not days. C. the government simply printing more money. D. None of the choices are true.
Exhibit 2-3 Production possibilities curve data A B C D E Capital goods 0 1 2 3 4 Consumer goods20 18 14 8 0 According to the data given in Exhibit 2-3, the production of 1 unit of capital goods and 20 units of consumer goods:
A. is possible but would be inefficient. B. may be a result of unemployment. C. may be a result of unused natural resources. D. is not feasible with current resources and technology.
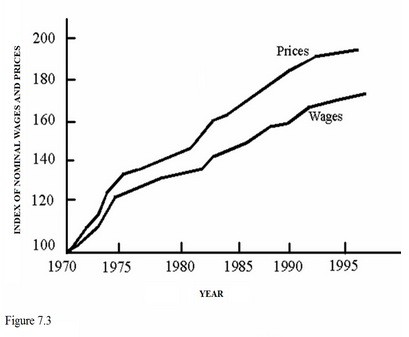 During the time period represented in Figure 7.3, the purchasing power of the average worker
During the time period represented in Figure 7.3, the purchasing power of the average worker
A. Decreased because nominal income decreased. B. Stay the same because COLAs reduced purchasing power. C. Decreased because real income decreased. D. Increased because nominal wages increased.