During the contraction phase of the business cycle,
a. prices fall relative to costs, reducing profit margins.
b. costs fall relative to prices, reducing profit margins.
c. prices fall relative to costs, increasing profit margins.
d. costs fall relative to prices, increasing profit margins.
a. prices fall relative to costs, reducing profit margins.
You might also like to view...
If the price of chocolate chip cookies falls, then
A) the supply curve of chocolate chip cookies shifts rightward. B) the supply curve of chocolate chip cookies shifts leftward. C) there is a movement downward along the supply curve of chocolate chip cookies. D) there is a movement upward along the supply curve of chocolate chip cookies.
An example of the ________ problem would be if Brian borrowed money from Sean in order to purchase a used car and instead took a trip to Atlantic City using those funds
A) moral hazard B) adverse selection C) costly state verification D) agency
Megan is trying to decide whether to buy house insurance for her home in Miami. Her house is worth $200,000 and analysts have determined that the average loss from a Hurricane could be $45,000. They have also determined there is a 50 percent chance that she will face a hurricane. Suppose Megan is a risk averse person with a utility-of-income function such as the one given below. If the policy costs $22,500, Megan will 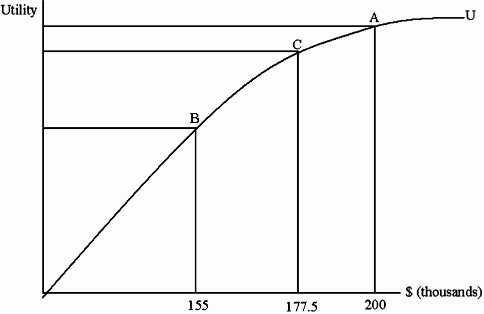
A. be indifferent between buying or not buying the insurance. B. not buy the insurance. C. buy the insurance. D. we can't say.
If prices are "sticky" in the short run, then
A. The economy will respond to demand shocks primarily through changes in output and employment B. The economy will respond to demand shocks primarily through changes in prices and inflation C. Prices will adjust to equalize the quantities demanded and supplied of goods and services D. Unemployment will not change in response to a demand shock