Draw a demand curve and label it D1. On the graph, illustrate an increase in demand and a decrease in demand, and label the curves D2 and D3, respectively. Starting on demand curve D1, explain the shift that would result from each of the following events:
a. an increase in income and the good is a normal good
b. an increase in income and the good is an inferior good
c. a decrease in the price of a substitute good
d. a decrease in the price of a complementary good
e. an increase in the taste for the good
f. a decrease in population
g. an increase in the expected future price of the good
a, d, e, and g would increase demand, causing a shift from D1 to D2
b, c, and f would decrease demand, causing a shift from D1 to D3
You might also like to view...
The economy pictured in the figure below has a(n) ________ gap with a short-run equilibrium combination of inflation and output indicated by point ________. 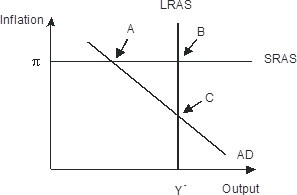
A. recessionary; B B. recessionary; C C. recessionary; A D. expansionary; A
Which of the following statements correctly differentiates between a model and a hypothesis?
A) Testing a hypothesis does not require data, whereas testing a model requires data. B) A model is a simplified representation of reality, whereas a hypothesis is a model's predictions. C) A hypothesis can be used to make predictions for the future, whereas a model can only explain the past. D) Testing a model requires data, whereas testing a hypothesis does not require data.
Peanut butter and jelly are complements for many consumers. Consider the market for peanut butter. If there is an increase in the price of jelly,
A) there is a shift in the supply curve for jelly. B) the price of peanut butter rises. C) the quantity of peanut butter increases. D) the demand curve for peanut butter does not shift; instead there is a movement along it. E) there is a movement along the supply curve of peanut butter.
When the percentage change in the quantity supplied is twice the percentage change in price, then supply is
A) elastic. B) inelastic. C) unit elastic. D) perfectly inelastic. E) perfectly elastic.