Star X has an apparent magnitude of 3, and star Y has an apparent magnitude of 13. How do they compare in observed brightness?
A) Star Y is 10,000 times brighter than star X. B) Star X is 10,000 times brighter than star Y.
C) Star Y is 10 times brighter than star X. D) Star X is 10 times brighter than star Y.
B
You might also like to view...
The acceleration of a cart rolling down an inclined plane (a ramp)
A) is approximately constant. B) increases with time. C) decreases with time.
Photon Energy: What is the wavelength of a photon having energy 2.00 eV? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ? s, 1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J)
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
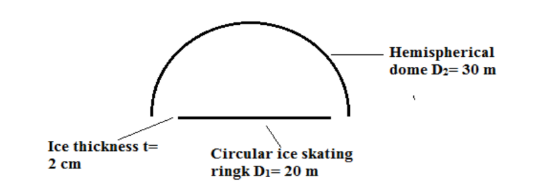
A circular ice skating rink, 20 m in diameter, is enclosed by a large hemispherical dome of diameter 30 m. Assuming that the ice is 2 cm thick, estimate the time it takes for the ice to melt if the refrigeration system of the rink fails. Make this calculation first with both the dome and the ice behaving as black bodies at respective temperatures of 20°C and 0°C. Then repeat with the water-ice having an emissivity of 0.3 and losing heat by natural convection to the air in the dome with a convection heat transfer coefficient of 15 W/(m2 K).
GIVEN
• Circular skating rink enclosed by hemispherical dome
• Diameter of the rink (D1) = 20 m
• Diameter of hemispherical dome (D2)= 30 m
• Temperature of dome and surrounding air (T2)= 200C
• Temperature of ice (T1) = 00C
FIND
Time it takes for ice to melt if the refrigeration system of rink fails considering (a) both dome and ice behaving as black bodies. (b) ice having emissivity of 0.3 and loosing heat by natural convection to air in dome with 2 15 W/(m K)
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
Latent Stefan-Boltzman’s heat of fusion constant for ice (Lf)= (? 334 KJ/kg )=5.67*10-8 W/(m2 K4)
In which case does an electric field do positive work on a charged particle?
a. A negative charge moves opposite to the direction of the electric field. b. A positive charge completes one circular path around a stationary positive charge. c. A positive charge is moved to a point of higher potential energy. d. A positive charge completes one elliptical path around a stationary positive charge.