A puck with a mass m1 = 28.0 g moving at 1.00 m/s approaches a stationary puck with a mass m2 = 102 g on an air table and they undergo a two-dimensional elastic collision
As a result of their interaction, the incident puck moves away with a speed v1 = 0.785 m/s and the other puck moves away with a speed v2 in a different direction. What is the angle between the velocities v1 and v2? A) 45.0°
B) 90.0°
C) 85.0°
D) 123°
E) 165°
D
You might also like to view...
The largest asteroid, and probably the only one to be a spherical "world," is:
A) Eros. B) Ida. C) Vesta. D) Ceres. E) Gaspra.
Just as a sustained flow of water in a hydraulic circuit needs a pump, in electric circuits the flow of charge needs
A) current. B) voltage. C) resistance.
The mean free path of a molecule is  m in an ideal gas at standard temperature and pressure. What is the mean free path when the pressure of the gas is doubled and the temperature is tripled?
m in an ideal gas at standard temperature and pressure. What is the mean free path when the pressure of the gas is doubled and the temperature is tripled?
a. 
b. 
c. 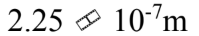
d. 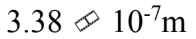
e. 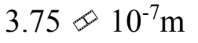
Main sequence stars lie at the top right corner of the H-R diagram
Indicate whether the statement is true or false