Populations of different kinds of organisms that interact with one another in a particular place are known as
A. ecosystems.
B. communities.
C. a biosphere.
D. a commune.
B. communities.
You might also like to view...
How does the proton motive force lead to production of ATP?
A) ATPase requires one proton to make one ATP. B) Protons must be pumped against a concentration gradient from outside of the cell into the cell to rotate the F0 subunit of ATPase for the F1 subunit to make ATP. C) Oxidative phosphorylation of ADP by ATP synthase requires protons as cofactors in the reaction. D) Translocation of three to four protons drives the F0 component of ATPase which in turn phosphorylates one ADP into ATP.
According to the figure, what is occurring during day 2?
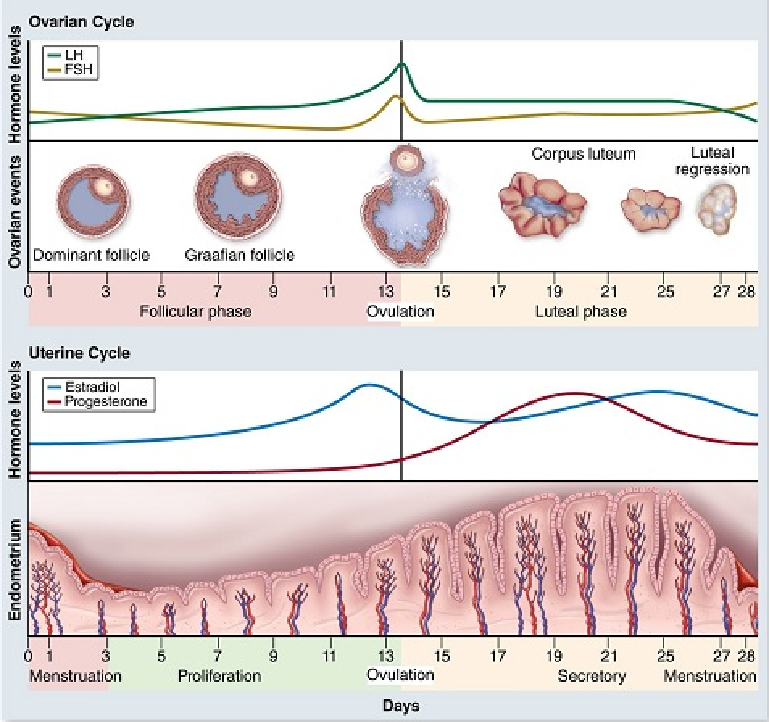
A. ovulation
B. release of corpus luteum
C. menstruation
D. luteal regression
E. copulation
Enzymes work by _____.
a) lowering the activation energy of a reaction and thus speeding up the reaction b) changing the free energy of a reaction and thus speeding up the reaction c) raising the activation energy of a reaction and thus speeding up the reaction d) lowering the delta G of a reaction and thus speeding up the reaction e) raising the delta g of a reaction and thus speeding up the reaction
The correct folding of proteins is necessary to maintain healthy cells and tissues
Unfolded proteins are responsible for such neurodegenerative disorders as Alzheimer's disease, Huntington's disease, and Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (the specific faulty protein is different for each disease). What is the ultimate fate of these disease-causing, unfolded proteins? (a) They are degraded. (b) They bind a different target protein. (c) They form structured filaments. (d) They form protein aggregates.