Historically, price discrimination was considered illegal in all instances. More recently, antitrust authorities have discovered that
A) price discrimination can increase the coverage of a market thereby increasing welfare.
B) price discrimination limits the coverage of a market thereby increasing welfare.
C) price discrimination limits the coverage of a market thereby decreasing welfare.
D) price discrimination can increase the coverage of a market thereby decreasing welfare.
A
You might also like to view...
The data below relates to a pure monopoly and the product it produces. What is the profit-maximizing output and price for this firm?
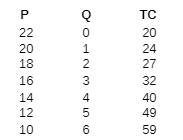
A. P = $15; Q = 3
B. P = $12; Q = 5
C. P = $18; Q = 2
D. P = $14; Q = 4
The most commonly used measure of changes in the cost of living for households
a. real GDP. b. the CPI. c. nominal GDP. d. the GDP deflator.
Suppose a monopolist is considering starting a $500,000 advertising campaign. The current demand for its product is given by
p = 150 - 3Q where Q is the quantity of output in thousands. If the monopolist undertakes the advertising campaign, it expects demand to increase to p = 200 - 4Q The (non-advertising) cost for the monopolist is C(Q) = 30Q. a. Determine whether the monopolist should undertake the advertising campaign assuming that it is correctly anticipating the potential increase in demand. b. What is the most the monopolist will invest towards this advertising campaign?
"Buy now, pay later" or "try it before you buy it" are examples of
a. Loss aversion b. Endowment effect c. Confirmation bias d. Anchoring bias