Briefly describe the World Trade Organization (WTO) rules on subsidies that affect exports of a product and responses by importing countries to such subsidies.
What will be an ideal response?
POSSIBLE RESPONSE: As a result of the agreements reached in the Tokyo and Uruguay Rounds of trade negotiations, the World Trade Organization (WTO) has established rules regarding export subsidies. WTO rules divide subsidies into either those that are linked directly to exports or those that are not linked directly to exports. Subsidies linked directly to exporting are prohibited, except export subsidies used by the lowest-income developing countries. An example of a subsidy that is directly linked to an export would be a firm that receives a tax break based on the amount that it exports. Subsidies that are not linked directly to exporting but still have an impact on exports are considered actionable. An example of a subsidy that is not directly linked to an export would be a government providing low-priced electricity to assist local firms in an industry that exports a portion of its production. If an importing country's government believes that a foreign country is using a prohibited subsidy or an actionable subsidy that is causing harm to an industry, the importing country can follow one of two procedures. The importing country can file a complaint with the WTO and use its dispute settlement procedure or, what is more common, use a national procedure similar to that used for dumping. If the importing country can show the existence of a prohibited or actionable subsidy and harm to its industry, the WTO rules permit the importing country to impose a countervailing duty. A countervailing duty is a tariff used to offset the price or cost advantage created by the subsidy to foreign exports.
You might also like to view...
Based on the figure below, the economy is initially at point A on the monetary policy reaction function (RF1) and the aggregate demand curve (AD1). The actual rate of inflation is ?' and the Federal Reserve's target inflation rate is ?*1. 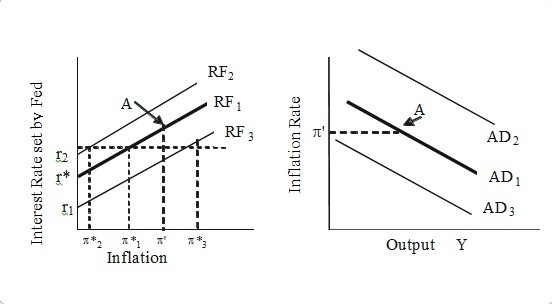 If the Federal Reserve lowers its target inflation rate to ?*2, then the Federal Reserve's monetary policy reaction function will ________ and the aggregate demand curve will ________.
If the Federal Reserve lowers its target inflation rate to ?*2, then the Federal Reserve's monetary policy reaction function will ________ and the aggregate demand curve will ________.
A. shift to RF3; shift to AD2 B. shift to RF2; shift to AD2 C. shift to RF2: shift to AD3 D. shift to RF3: shift to AD3
The demand for money will fall for each of the following reasons, except
A) more ATMs. B) higher real GDP. C) lower interest rates on transactions accounts at banks. D) more risky banks.
The aggregate demand curve tends to be
a. vertical. b. horizontal. c. upward sloping. d. downward sloping.
Governments typically intervene in markets
a. to bring the market price to its equilibrium level b. to shift the price away from its equilibrium level c. only to increase the market price d. only to increase the market output e. because in some markets, supply and demand do not generate their own equilibrium price