Average cost equals
A. change in total cost/change in quantity.
B. total cost/quantity.
C. total cost ? total variable cost.
D. total cost ? total fixed cost.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Suppose the economy is operating below potential output. If policy makers try to avoid a budget deficit by raising taxes or reducing government spending, these actions would
A) make a recession worse. B) increase inflation. C) negate the multiplier effect. D) help pull an economy out of a depression.
Before the financial crisis of 2008:
A. the 2.5 percent inflation target was seen as a precise target. B. the 2.5 percent inflation target was seen as an upper bound. C. inflation was not seen as a target. D. the 2.5 percent inflation target was seen as a lower bound.
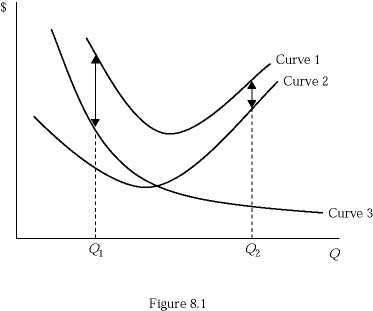 Refer to Figure 8.1, which shows a family of average cost curves. The average fixed cost curve is represented by:
Refer to Figure 8.1, which shows a family of average cost curves. The average fixed cost curve is represented by:
A. Curve 1. B. Curve 2. C. Curve 3. D. the vertical sum of curve 1 and curve 2.
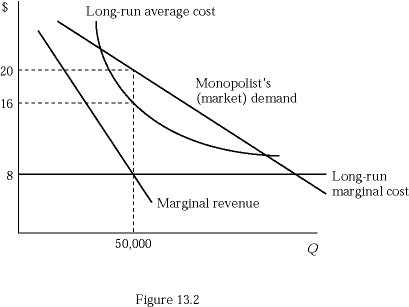 Consider an unregulated monopoly in Figure 13.2. If that monopoly sets its price equal to its marginal cost, it would:
Consider an unregulated monopoly in Figure 13.2. If that monopoly sets its price equal to its marginal cost, it would:
A. earn negative profits. B. earn maximum profits. C. earn zero profits. D. earn small, but greater than zero, profits.