Assume that the central bank purchases government securities in the open market. If the nation has highly mobile international capital markets and a flexible exchange rate system, what happens to the GDP Price Index and net nonreserve-related international borrowing/lending in the context of the Three-Sector-Model?
a. The GDP Price Index falls, and net nonreserve-related international borrowing/lending becomes more negative (or less positive).
b. The GDP Price Index and net nonreserve-related international borrowing/lending remain the same.
c. The GDP Price Index falls, and net nonreserve-related international borrowing/lending becomes more positive (or less negative).
d. The GDP Price Index rises, and net nonreserve-related international borrowing/lending becomes more negative (or less positive).
e. The GDP Price Index rises, and net nonreserve-related international borrowing/lending becomes more positive (or less negative).
.D
You might also like to view...
Classicals argue that an adverse supply shock would
A) raise neither the natural rate of unemployment nor the actual rate of unemployment. B) raise the actual rate of unemployment, but not the natural rate of unemployment. C) raise the natural rate of unemployment, but not the actual rate of unemployment. D) raise both the natural rate of unemployment and the actual rate of unemployment.
Refer to the table below. If the profit for each unit of paper product is $3.00 and the profit for each unit of lumber is $13.50, what is the marginal benefit for each unit of lumber produced?
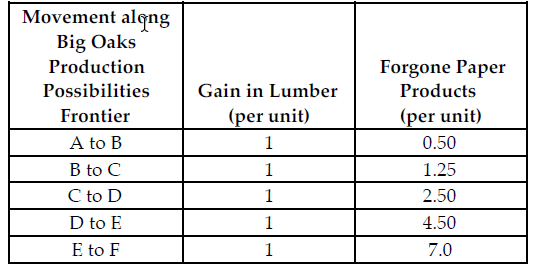
Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amount of paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable proportions. The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.
A) $13.50
B) $16.50
C) $10.50
D) $3.00
The type of good that is most likely to be subject to market failure is:
A. a public good. B. a private good. C. an uncommon resource. D. a factor of production
Walter builds birdhouses. He spends $5 on the materials for each birdhouse. He can build one in 30 minutes. He is semi-retired but earns $8 per hour at the local hardware store. He can sell a birdhouse for $20 each. An accountant would calculate the total profit for one birdhouse to be
a. $7. b. $11. c. $12. d. $15.