Spherical Mirrors: An object is 10 cm in front of a concave spherical mirror with a focal length of magnitude 3.0 cm. Where is the image?
A. 13 cm from the mirror
B. 7.0 cm from the mirror
C. 4.3 cm from the mirror
D. 3.3 cm from the mirror
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
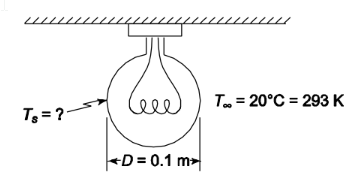
Only 10% of the energy dissipated by the tungsten filament of an incandescent lamp is in the form of useful visible light. Consider a 100 W lamp with a 10 cm spherical glass bulb. Assuming an emissivity of 0.85 for the glass and ambient air temperature of 20°C, what is the temperature of the glass bulb?
GIVEN
• A spherical glass light bulb in air
• Bulb power consumption (P) = 100 W
• 10% of energy is in the form of visible light
• Diameter (D) = 10 cm = 0.1 m
• Bulb emissivity (?) = 0.85
• Ambient temperature (T?) = 20°C = 293 K
FIND
• The temperature of the glass bulb (Ts)
ASSUMPTIONS
• Ambient air is till
• The bulb has reached steady state
• The surrounding behave as a black body at T?
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
Boltzmann constant (?) = 5.7 × 10–8 W/(m2 K4).
All around the world, ancient cultures celebrated heroes, gods, and mythical beasts by naming groups of stars called _____
A) satellites B) constellations C) wormholes D) comets
An apparent westward motion of a planet in the sky compared to the background stars (as viewed from Earth) when observed on successive nights is referred to as
a. epicycle. b. retrograde motion. c. prograde motion. d. heliocentric motion. e. deferent.
The light from an object moving tangentially (to your left or right) will exhibit:
A) a blueshift. B) a redshift. C) a shift in peak wavelength towards the red. D) a shift in peak wavelength towards the blue. E) no shift.