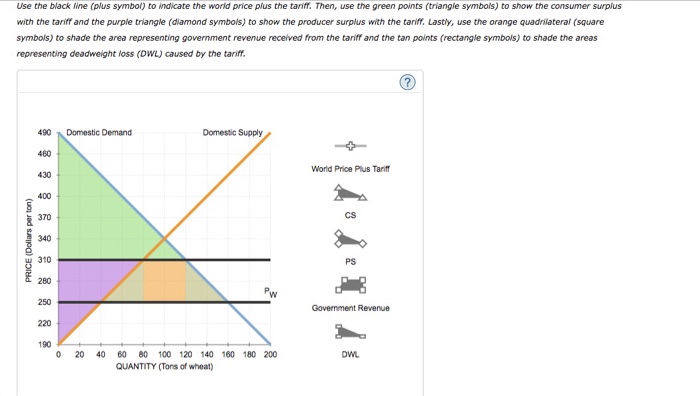
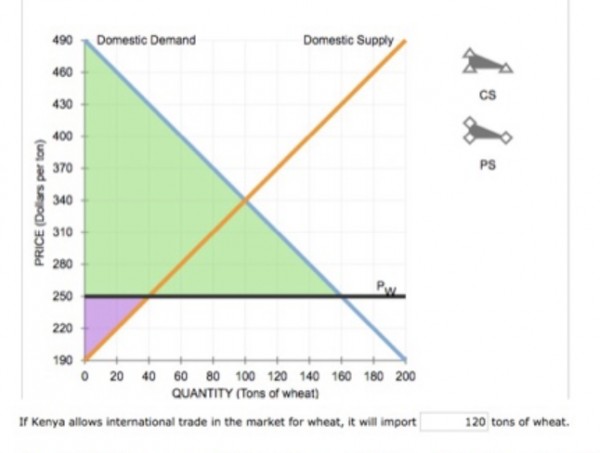
Suppose Kenya is open to free trade in the world market for wheat. Because of Kenya’s small size, the demand for and supply of wheat in Kenya do not affect the world price. The following graph shows the domestic wheat market in Kenya. The world price of wheat is PW = $250 per ton.
On the following graph, use the green triangle (triangle symbols) to shade the area representing consumer surplus (CS) when the economy is at the free-trade equilibrium. Then, use the purple triangle (diamond symbols) to shade the area representing producer surplus (PS).
Ans:
Under free trade:
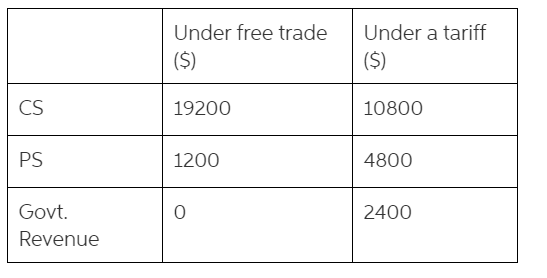
CS = area of green triangle = (490 - 250) x 160/2
PS = area of purple triangle = (250 - 190) x 40/2
Under a tariff:
CS = area of green triangle = $10800
PS = area of purple triangle =$4800
Government revenue = area of orange square = $2400
Based on your analysis, as a result of the tariff, Kenya's consumer surplus decreases by $8400, producer surplys increases by $3600, and the government collects $2400 in revenue. Therefore, the net welfare effect is a deadweight loss of $2400 (Difference in the two columns calculated above)
You might also like to view...
Refer to Table 18-9. Sylvia is a single taxpayer with an income of $70,000. What is her marginal tax rate and what is her average tax rate?
A) marginal tax rate = 8%; average tax rate = 19.3% B) marginal tax rate = 30%; average tax rate = 22.5% C) marginal tax rate = 20%; average tax rate = 30% D) marginal tax rate = 30%; average tax rate = 30%
Some claim that the long and agonizing periods of speculation preceding exchange rate realignments would
A) not occur under fixed exchange rate regime. B) not occur under floating. C) become more severe under currency board. D) become less severe under floating. E) be prolonged under floating.
A perfectly competitive firm has a horizontal demand curve because it can sell as much as it wants at the market price
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
The free-rider problem arises because:
A. once provided, a public good is available to all regardless of whether they paid for it. B. poor people cannot afford to contribute to public goods. C. enforcement of tax laws is inadequate. D. people disagree with how the government spends its money.