Because the U.S. poverty line is an absolute measure rather than a relative one, the official U.S. poverty rate:
A. increased steadily when there was economic growth that raised the incomes of low-income families.
B. fell steadily when there was economic growth that raised the incomes of low-income families.
C. fell steadily when there was economic growth that caused inequality to grow among the population.
D. increased steadily when there was economic growth that caused inequality to decline across the population.
B. fell steadily when there was economic growth that raised the incomes of low-income families.
You might also like to view...
Bracket creep forces taxpayers to pay a larger percentage of their income in taxes when which of the following occurs?
(a) The emergence of high unemployment (b) Inflation (c) Deflation (d) The growth of trade deficit(s)
In a strike, what does the union have to lose? What does management lose?
Using Figure 1 above, if the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD1 to AD2 the result in the long run would be: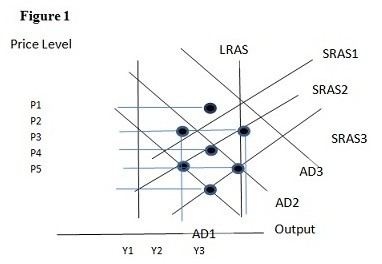
A. P1 and Y2. B. P2 and Y2. C. P3 and Y1. D. P2 and Y3.
Consider a two-country, two-commodity model. The table below shows the units of Good X and Good Y produced in Country A and Country B per labor hour. Country B has an absolute advantage in the production of ProductivityCountry ACountry BGood X1.000.50Good Y0.200.70
A. only Good X. B. neither Good X nor Good Y. C. only Good Y. D. both Good X and Good Y.