When a country imposes an import quota, its exchange rate
a. rises because the supply of dollars in the market for foreign-currency exchange falls.
b. falls because the supply of dollars in the market for foreign-currency exchange rises.
c. rises because the demand for dollars in the market for foreign-currency exchange rises.
d. falls because the demand for dollars in the market for foreign-currency exchange falls.
c
You might also like to view...
What is the difference between an open outcry auction and a sealed bid auction?
What will be an ideal response?
If the price of Pepsi-Cola increases from 50 cents to 60 cents per can and the quantity demanded decreases from 100 cans to 50 cans, then the demand for Pepsi-Cola is
a. unit elastic b. perfectly elastic c. perfectly inelastic d. relatively elastic e. relatively inelastic
Figure36-9
?
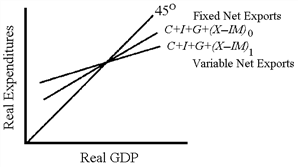
A. (X? IM)1 line indicates that net exports decline as GDP rises. B. (X? IM)1 line indicates that net exports rise as GDP rises. C. multiplier is greater for the (X? IM)1 line. D. (X? IM)1 line indicates that tariffs, quotas, and other trade barriers are keeping net exports below their full potential.
If expectations are rational,
a. a predictable change in inflation can make the expected inflation rate deviate from the actual rate. b. unemployment can exceed the full-employment rate even in the long run. c. the difference between the actual inflation rate and the expected inflation rate must be a purely random number. d. the inflation rate cannot be reduced without a period of high unemployment because the Phillips curve is downward sloping.