What is the Federal funds rate and how does the Fed target it?
What will be an ideal response?
The Federal funds rate is the interest rate charged on overnight loans made from banks with temporary excess reserves to banks with reserve deficiencies.
The Fed uses its ability to manipulate the supply of excess reserves in the banking system to designate and make adjustments to maintain the Federal funds rate. After the Fed decides on the rate it wants, it determines how many loadable funds banks will demand at that interest rate and supply it. If demand should increase (demand curve shifts out), the Fed will engage in open-market operations to increase the availability of reserves to maintain that rate. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts in), the Fed will engage in open-market operations to decrease the availability of reserves to maintain the target rate.
You might also like to view...
Using year-by-year data from 1987-2007 shows that
A) there is a strong positive relation between average Latin American money-supply growth and inflation. B) there is a strong negative relation between average Latin American money-supply growth and inflation. C) there is a strong positive relation between average Latin American money-supply growth and deflation. D) it is difficult to find a strong positive relation between average Latin American money-supply growth and inflation. E) there is a weak positive relation between average Latin American money-supply growth and inflation.
This graph depicts the demand for a normal good.
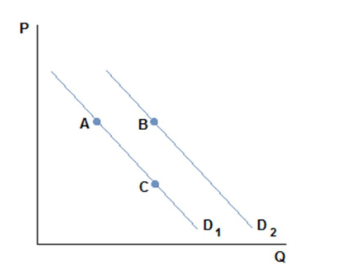
A movement from A to C in the graph shown might be caused by:
A. an increase in price.
B. a decrease in price.
C. an increase in income.
D. a decrease in income.
Which statement is most accurate about the real GDP per capita of different nations between 1980 and 2006?
a. The real GDP per capita of the US ranks in the middle of the other major industrialized nations. b. The US had the highest real per capita GDP at the beginning of the period, but by the end of the period many other industrialized had caught up to the US. c. The US had the highest real per capita GDP throughout the period and on average, the other major industrialized nations did not significantly close the gap. d. At the beginning of the period, the US had a real GDP per capita equal to the average of the major industrialized nations, but by 2006 the US had moved into first place.
The present value of $1 million to be received in the future will
a. increase if the interest rate rises. b. increase if the payment is received at a more distant time in the future. c. be greater than $1 million. d. increase if the interest rate were to fall from 8 percent to 4 percent.