A 2.0-kg object moving with a velocity of 5.0 m/s in the positive x direction strikes and sticks to a 3.0-kg object moving with a speed of 2.0 m/s in the same direction. How much kinetic energy is lost in this collision?
a. 2.4 J
b. 9.6 J
c. 5.4 J
d. 0.6 J
e. 6.0 J
c
You might also like to view...
Derive an equation for the net rate of radiant heat transfer from surface 1 in the system shown in the accompanying sketch. Assume that each surface is at a uniform temperature and that the geometrical shape factor F1–2 is 0.1.
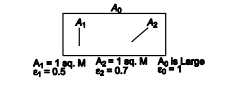
GIVEN
? The system shown above
FIND
? An expression for the net rate of radiant heat transfer from surface 1 (q1)
ASSUMPTIONS
? Steady state
? A1 and A2 are gray, A0 is black
? Each surface is at a uniform temperature
? The shape factor F12 = 0.1
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
To what do the terms node and antinode refer?
a) antinodes are points of no oscillation; nodes are points of maximum oscillation b) nodes are points of no oscillation; antinodes are points of maximum oscillation
Why does the temperature of the gas between galaxies in galaxy clusters tell us about the mass of the cluster?
A) The temperature tells us the average speeds of the gas particles, which are held in the cluster by gravity, so we can use these speeds to determine the cluster mass. B) Temperature is always directly related to mass, which is why massive objects are always hotter than less massive objects. C) The temperature of the gas tells us the gas density, so we can use the density to determine the cluster's mass. D) The question is nonsense; gas temperature cannot possibly tell us anything about mass.
Suppose you were to try to create a proton-antiproton pair by annihilation of two very high-energy gamma rays of the same wavelength heading toward each other. The proton and the anti-proton have the same masses, but opposite charges
What would be the minimum energy needed for each photon? (e = 1.60 × 10-19 C, mproton = 1.67 × 10-27 kg, c = 3.00 × 108 m/s) A) 223 MeV B) 1880 MeV C) 12.2 MeV D) 1.022 MeV E) 939 MeV