Refer to Figure 23-1. At point L in the figure above, which of the following is true?
A) Actual inventories are greater than planned inventories.
B) The economy has achieved macroeconomic equilibrium.
C) Aggregate expenditure is greater than GDP.
D) GDP will be increasing.
A
You might also like to view...
Which of the following will most likely have the greatest effect on an individual’s consumption function?
A. Winning a small amount in the lottery B. A one-time tuition grant C. A week of high overtime pay D. An inheritance paying a modest annual dividend
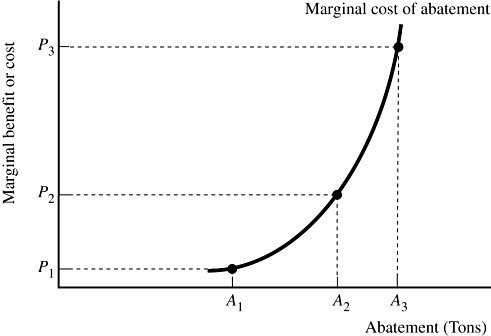 Figure 16.1A firm that generates pollution is illustrated in Figure 16.1. The government has chosen to impose a pollution tax equal to P2. From the firm's point of view, the marginal benefit of abatement is:
Figure 16.1A firm that generates pollution is illustrated in Figure 16.1. The government has chosen to impose a pollution tax equal to P2. From the firm's point of view, the marginal benefit of abatement is:
A. avoiding the pollution tax imposed by the government. B. the positive publicity the firm will receive by having a "green" production plant. C. the reciprocal of the marginal cost of abatement. D. zero because abatement benefits the general public, not the firm.
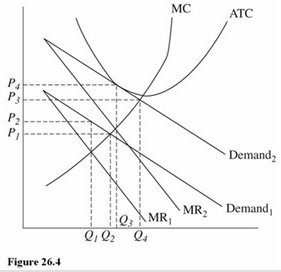 Refer to Figure 26.4 for a monopolistically competitive firm. In the long run this firm is most likely to face
Refer to Figure 26.4 for a monopolistically competitive firm. In the long run this firm is most likely to face
A. A demand curve between Demand1 and Demand 2. B. Demand2 and MR2. C. Demand1 and MR2. D. Demand1 and MR1.
GDP and derivative measures like GDP per capita are frequently criticized because of its limited scope. While it is limited in what id directly measures, these criticisms are often misplaced because
A) GDP is not really emphasized in macroeconomics anymore; instead, substitute measures have become more widely used B) GDP is closely correlated with non-monetary outcomes that people clearly value such as life expectancy, infant mortality, and literacy C) GDP actually does directly incorporate the value and quality of a variety of items that are not actually bought and sold such as leisure D) GDP in nominal terms does not include household production or leisure but real GDP does