Refer to Game Matrix I. What are the dominant strategies in this game?

a. A's dominant strategy is ?, and B's dominant strategy is ?.
b. A's dominant strategy is ?, but B does not have a dominant strategy.
c. B's dominant strategy is ?, but A does not have a dominant strategy.
d. Neither player has a dominant strategy.
b. A's dominant strategy is ?, but B does not have a dominant strategy.
You might also like to view...
When interest rate rise consumers will
A) compare loan payments with the desirability of goods in the future and increase consumption. B) compare loan payments with the desirability of goods today and increase consumption. C) wait to borrow funds when interest rates fall. D) none of above.
Suppose a recession overseas reduces a country's exports. Which curve(s) in the aggregate demand and aggregate supply model would be affected, and which way would it (they) shift?
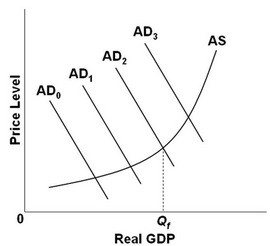 Refer to the above diagram, in which Qf is the full-employment output. If the economy's current aggregate demand curve is AD0, it would be appropriate for the government to:
Refer to the above diagram, in which Qf is the full-employment output. If the economy's current aggregate demand curve is AD0, it would be appropriate for the government to:
A. increase government expenditures or reduce taxes. B. reduce government expenditures or increase taxes. C. reduce government expenditures and taxes by equal-size amounts. D. reduce unemployment compensation benefits.
Consider a world of two countries producing only wheat and cloth. In one hour, residents of Country A can produce 1 unit of wheat and 0.5 unit of cloth, whereas residents of Country B can produce 0.3 unit of wheat and 0.4 unit of cloth. Country A should
export A) wheat and cloth; country B should not export anything. B) wheat and country B should export cloth. C) nothing and country B should export both wheat and cloth. D) cloth and country B should export wheat.