You are looking for a new electrical appliance that will last a long time. You are considering buying a high-efficiency model that uses an average of 60 W
of power and
costs $800 or a lower efficiency model that uses an average of 90 W and costs $600 . If the
cost of electricity is $0.10/kWh and the appliances are operated continuously, how much
money will you have saved by purchasing and operating the high efficiency model over the
low efficiency model after 15 years?
The total cost of the more efficient refrigerator will be
$800.00 + 60 W x 15 yr x 8760 h/yr x $0.10/kWh
= $800.00 + 788.4 kWh x $0.10/kWh = $878.84
The total cost of the lower-efficiency model is
$600.00 + 90 W x 15 yr x 8760 h/yr x $0.10/kWh
= $600.00 + 1182.6 kWh x $0.10/kWh = $718.26
Far from saving money, it would cost you about $160 more for the more efficient model in
this comparison. This problem should impress on the student the need to study the energy
ratings and the additional costs involved.
Actually, the power given for the less-efficient model is probably too low (and some models
do even better than the quoted high-efficiency power consumption). If we used 120 watts
for the less-efficient refrigerator, though, we'd still save by buying the cheaper model—
although only about $2 . Because a typical refrigerator lasts 19 yr, the more energy-efficient
model would save money over its entire lifetime.
You might also like to view...
Find the final equilibrium temperature when 20.0 g of milk at 10.0°C is added to 160 g of coffee at 90.0°C. (Assume the specific heats of coffee and milk are the same as water and neglect the heat capacity of the container, and cwater = 1.00 cal/g•°C = 4186 J/kg•°C)
a. 85.3°C c. 71.4°C b. 81.1°C d. 66.7°C
What is the period for a frequency of 60 Hz?
A. 60 s B. (1/60) s C. 120 s D. (1/120) s E. (1/377) s
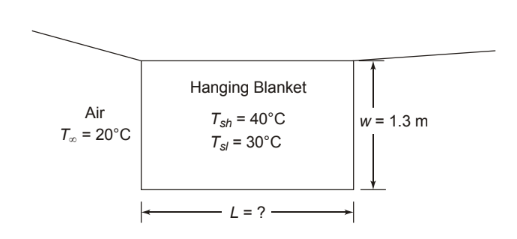
An electric heating blanket is subjected to an acceptance test. It is to dissipate 400 W on the high setting when hanging in air at 20°C. (a) If the blanket is 1.3-m-wide: what is the length required if its average temperature at the high setting is to be 40°C, (b) If the average temperature at the low setting is to be 30°C, what rate of dissipation is possible?
GIVEN
• An electric blanket hanging in air
• Heat dissipation rate (qh) = 400 W
• Air temperature (T?) = 20°C
• Blanket width (w) = 1.3 m
• Average temperatures ? High (Tsh) = 40°C
? Low (Ts1) = 30°C
FIND
(a) The length of the blanket (L) (b) Heat dissipation rate on the low setting (q1) ASSUMPTIONS
• Air is still
• Moisture in the air has a negligible effect
• Blanket is hung vertically with its 1.3 m sides vertical
SKETCH
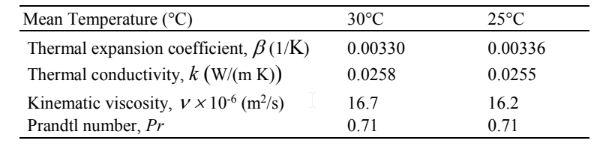
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
for dry air at the mean temperatures for the two settings
A body at the end of a spring oscillates up and down ten times in five seconds. The period of oscillation is
a. 0.5 s. b. 2 s. c. 5 s. d. 10 s. e. not determinable.