If a 20 W laser beam, which has an initial diameter of 2.0 mm, spreads out to a diameter of 2.0 m after traveling 10,000 m, what is the initial Erms of the beam?
a. 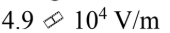
b. 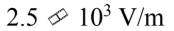
c. 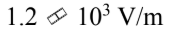
d. 
e. 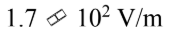
a. 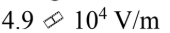
You might also like to view...
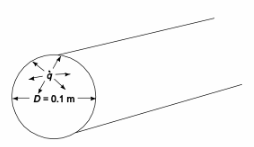
Experiments have been performed on the temperature distribution in a homogeneous long cylinder (0.1 m diameter, thermal conductivity of 0.2 W/(m K) with uniform internal heat generation. By dimensional analysis, determine the relation between the steady-state temperature at the center of the cylinder Tc the diameter, the thermal conductivity, and the rate of heat generation. Take the temperature at the surface as you datum. What is the equation for the center temperature if the difference between center and surface temperature is 30°C when the heat generation is 3000 W/m3?
GIVEN
A homogeneous long cylinder with uniform internal heat generation
Diameter (D) = 0.1 m
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.2 W/(m K)
Difference between surface and center temperature (Tc – Ts) = 30°C
Heat generation rate q = 3000 W/m3
FIND
(a) Relation between center temperature (Tc), diameter (D), thermal conductivity (k), and rate of heat
generation q
(b) Equation for the center temperature for the given data
ASSUMPTIONS
Steady state
One dimensional conduction in the radial direction
SKETCH
In an analysis relating Bohr's theory to the de Broglie wavelength of electrons, when an electron moves from the n = 1 level to the n = 3 level, the circumference for its orbit becomes 9 times greater. This occurs because:
a. the wavelength of the electron becomes nine times as long. b. there are triple as many wavelengths, and each wavelength is triple in length. c. there are nine times as many wavelengths in the new orbit. d. the electron is moving nine times as fast.
John throws a rock down with speed 11 m/s from the top of a 25-m tower. If g = 9.8 m/s2 and air resistance is negligible, what is the rock's speed just as it hits the ground?
a. 19 m/s b. 25 m/s c. 610 m/s d. 22 m/s e. 12 m/s
The form of heat transfer that doesn't depend on a medium is
A) conduction. B) convection. C) radiation. D) all of the above