One way of stating the principle of relativity is:
A) Light has the same speed for all nonaccelerated observers.
B) Experiments conducted entirely within your own lab will come out differently, depending on the state of motion of the lab relative to other reference frames.
C) Observers that are accelerated will see light beams move at something other than lightspeed.
D) Unless you look outside, you cannot tell how fast you are going.
E) The speed of light is relative to the motion of the observer, provided that the observer is not accelerated.
D
You might also like to view...
How did the geocentric model and the heliocentric model of the universe explain retrograde motion?
What will be an ideal response?
Addition by 1. Components: Vector 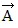 has a magnitude of 6.0 m and points 30° north of east. Vector
has a magnitude of 6.0 m and points 30° north of east. Vector 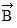 has a magnitude of 4.0 m and points 30° west of north. The resultant vector
has a magnitude of 4.0 m and points 30° west of north. The resultant vector 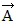 +
+ 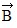 is given by
is given by
A. 9.8 m at an angle of 64° east of north. B. 9.8 m at an angle of 26° north of east. C. 7.2 m at an angle of 26° east of north. D. 3.3 m at an angle of 26° north of east. E. 3.3 m at an angle of 64° east of north.
An unbalanced force always produces
a) a circular motion. b) an acceleration. c) a state of equilibrium. d) a constant velocity.
A particle (charge 7.5 mC) is released from rest at a point on the x axis, x = 10 cm. It begins to move due to the presence of a 2.0-mC charge which remains fixed at the origin. What is the kinetic energy of the particle at the instant it passes the point x = 1.0 m?
a. 3.0 J b. 1.8 J c. 2.4 J d. 1.2 J e. 1.4 J