A projectile is shot horizontally at 23.4 m/s from the roof of a building 55 m tall and experiences negligible air resistance. (a) Determine the time necessary for the projectile to reach the ground below
(b) Determine the distance from the base of the building that the projectile lands. (c) Determine the horizontal and vertical components of the velocity just before the projectile reaches the ground.
(a) 3.4 s (b) 78 m (c) vhoriz = 23.4 m/s, vvert = 33 m/s downward
You might also like to view...
For the typical "household ac voltage" of 120 V, what is the amplitude of the emf?
A. 120 V B. 240 V C. 60.0 V D. 170 V E. 330 V
What are the basic building blocks of proteins?
a. Amino acids b. Starches c. Sugars d. Carboxylic acids
The wedge-shaped cavity shown in the accompanying sketch consists of two long strips joined along one edge. Surface 1 is 1-m-wide, has an emittance of 0.4, and has a temperature of 1000 K. The other wall has a temperature of 600 K. Assuming gray diffuse processes and uniform flux distribution, calculate the rate of energy loss from surface 1 and 2 per meter length.
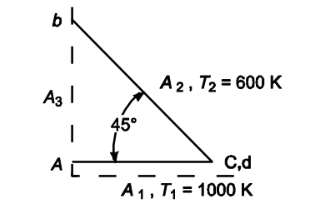
GIVEN
• The wedge shaped cavity shown above
• Width of A1 (W1) = 1 m
• Emittance of A1 (?1) = 0.4
• Temperature of A1 (T1) = 1000 K
• Temperature of A2 (T2) = 600 K
• A2 is black
FIND
• The rate of energy loss from A1 and A2 per meter length (q1/L and q2/L)
ASSUMPTIONS
• Enclosure temperature (Te) = 0 K
• Gray diffuse processes
• Uniform flux distribution
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
the Stephan-Boltzmann constant (?) = 5.67 × 10–8 W/(m2 K4)
_____, the largest of Saturn's moons, has an atmosphere composed mostly of nitrogen with traces of argon and methane
A) Ganymede B) Miranda C) Europa D) Titan