A CD with a diameter of 12.0 cm starts from rest and with a constant angular acceleration of 1.0 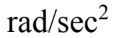 acquires an angular velocity of 5.0 rad/sec. The CD continues rotating at 5.0 rad/sec for 15.0 seconds and then slows to a stop in 12.0 second with a constant angular deceleration. What is the centripetal acceleration of a point 4.0 cm from the center at the time 15.0 seconds from the start?
acquires an angular velocity of 5.0 rad/sec. The CD continues rotating at 5.0 rad/sec for 15.0 seconds and then slows to a stop in 12.0 second with a constant angular deceleration. What is the centripetal acceleration of a point 4.0 cm from the center at the time 15.0 seconds from the start?
A. 0.5 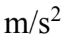
B. 1.0 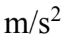
C. 1.8 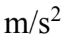
D. 2.0 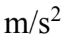
E. 2.6 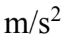
B. 1.0 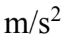
You might also like to view...
An atom that has lost or gained one or more electrons is called a(n) ____
a. ion b. isotope c. nucleus d. molecule e. electron
A proton, moving east, enters a magnetic field. Because of this magnetic field the proton curves downward. We may conclude that the magnetic field must have a component
A) towards the south. B) towards the north. C) towards the west. D) upward. E) downward.
A horizontal disk with a radius of 10 cm rotates about a vertical axis through its center. The disk starts from rest at t = 0 and has a constant angular acceleration of 2.1 rad/s2 . At what value of t will the radial and tangential components of the linear acceleration of a point on the rim of the disk be equal in magnitude?
a. 0.55 s b. 0.63 s c. 0.69 s d. 0.59 s e. 0.47 s
The ground state electronic configuration for magnesium is 1s22s22p63s2 . Which of the following would most likely result in an element being chemically similar to magnesium?
a. the valence subshell having 2 electrons b. the valence electron being an s2 electron c. the valence electron being a p2 electron d. the valence electron having principal quantum number 3