The McCallum management principles advocate the use of
a. time-motion study to determine the most productive way to perform job-tasks.
b. employee stock-purchase programs.
c. internal accounting systems and performance evaluations.
d. leveraged buy-outs to increase the firm's control of an industry.
c. internal accounting systems and performance evaluations.
You might also like to view...
What does "diminishing marginal utility" mean?
What will be an ideal response?
Which of the following statements best describes consumer confidence as measured by the consumer confidence index, from just prior to the Great Recession until late 2008.
a. According to the consumer confidence index, consumer confidence averaged around 90 prior to the Great Recession, and then it fell to below 50 in late 2008, which was the lowest it had been since 1980. b. According to the consumer confidence index, consumer confidence averaged around 80 prior to the Great Recession, and then it fell to below 50 in late 2008, which was the lowest it had been since 1980. c. According to the consumer confidence index, consumer confidence averaged around 90 prior to the Great Recession, and then it fell to below 60 in late 2008, which was the lowest it had been since 1980. d. According to the consumer confidence index, consumer confidence averaged around 80 prior to the Great Recession, and then it fell to below 60 in late 2008, which was the lowest it had been since 1980.
If the price of a soda is $0.50, and the marginal utility of the first soda consumed is valued at $2, then the consumer surplus of that first soda is
a. $0.50 b. $1.50 c. $2.00 d. $2.50 e. $4.00
Refer to the diagrams for two separate product markets. Assume that society's optimal level of output in each market is Q 0 and that government purposely shifts the market supply curve from S to S 1 in diagram (a) on the left and from S to S 2 in
diagram (b) on the right. We can conclude that the government is correcting for:
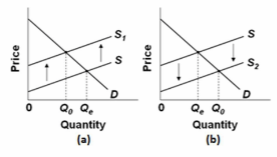
A. negative externalities in diagram (a) and positive externalities in diagram (b).
B. positive externalities in diagram (a) and negative externalities in diagram (b).
C. negative externalities in both diagrams.
D. positive externalities in both diagrams.