For which of the following firms is patent protection of vital importance?
A) software firms B) pharmaceutical firms
C) furniture producers D) auto makers
B
You might also like to view...
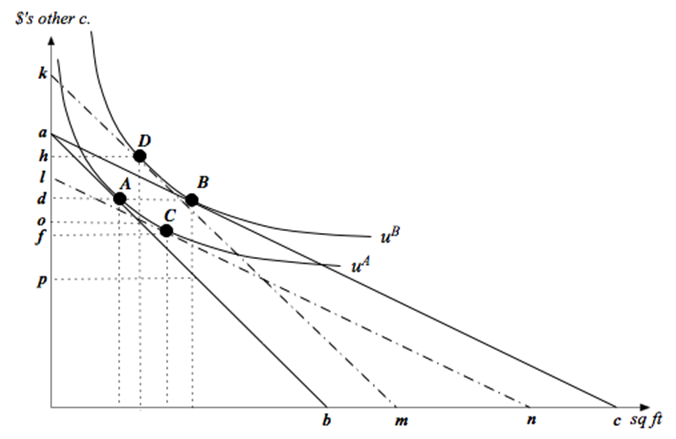
Consider a household with income I and two goods to choose from - square feet of housing (x1) and dollars of other consumption (x2). The annual price per square foot of housing is p, and the household's tastes can be described by the utility function u(x1,x2)= x10.25x20.75. a. How much housing and other goods will the household demand as a function of p and I. b. Suppose income is $100,000 and the price of housing is $10 per square foot. Then the government introduces a subsidy that lowers the housing price to $5 per square foot. In the attached graph, let the solid lines denote the budget lines of the household before and after the subsidy. What are the values of the intercept terms a, b and c in the graph?
c. How much of each good does the household consume at bundle A- i.e. what are the values of d and e in the graph. How much would the household consume of each good after the subsidy?
d. Answer this part in terms of letters on the vertical axis of the graph. What is the most this household would be willing to pay in cash to get this price subsidy? If a household already had the subsidy (without having paid any cash to get it), what is the least that we would have to pay the household in cash for the household to be willing to give up the subsidy?
e. The expenditure function for this household is approximately E(p,u)=1.755p0.25u. Calculate dollar values for the first question in part (d).
f. What is the dollar value for the second question in part (d)?
g. If the subsidy is put in place (without the household making any cash payments to get it), how much will the subsidy cost the government? Express this as a distance in the graph as well as a dollar value.
h. Explain intuitively why there is a deadweight loss of implementing the subsidy - and then calculate the dollar value of the deadweight loss.
i. Calculate the bundles C and D in the graph - i.e. calculate the values for f, g, h and i. (Hint: You can do this a number of different ways - but the quickest way would be to use your answers to parts (e) and (f).)
What will be an ideal response?
Refer to the figure above. A change in the budget constraint from B1 to B2 indicates:
A) an increase in the price of sweaters. B) a decrease in the price of sweaters. C) an increase in the consumer's income. D) a decrease in the consumer's income.
If the Fed wants to depreciate the U.S. dollar against the British pound, it will ________
A) sell foreign exchange B) decrease the money supply C) sell British pounds D) sell U.S. dollars
The free-rider problem arises if goods are
A. nonrivalrous in consumption. B. rivalrous in consumption. C. nonexcludable. D. excludable. E. a and d