For a given price level, a downward shift of the expenditures schedule corresponds to an
a. inward shift of the aggregate demand curve.
b. outward shift of the aggregate demand curve.
c. outward shift of the aggregate supply curve.
d. inward shift of the aggregate supply curve.
a
You might also like to view...
A key finding of the economic analysis of financial structure is that
A) the existence of the free-rider problem for traded securities helps to explain why banks play a predominant role in financing the activities of businesses. B) while free-rider problems limit the extent to which securities markets finance some business activities, nevertheless the majority of funds going to businesses are channeled through securities markets. C) given the great extent to which securities markets are regulated, free-rider problems are not of significant economic consequence in these markets. D) economists do not have a very good explanation for why securities markets are so heavily regulated.
To say that there is a scarcity of gold means that:
a. gold prices will fall in the future. b. there is not enough gold to satisfy people's demand for it at a zero price. c. there are very few substitutes for gold. d. gold is very expensive. e. the demand for gold is changing.
The figure below represents the effects in the labor markets due to migration. Here, the world has been divided into a high-income "North" (left panel) and a low-income "South" (right panel). Dn and Sn are the labor demand and the labor supply curves in North. Ds and (Sr + Smig) are the labor demand and pre-migration labor supply curves in South. Sr is the post-migration labor supply curve in South. The value c is the cost of migrating.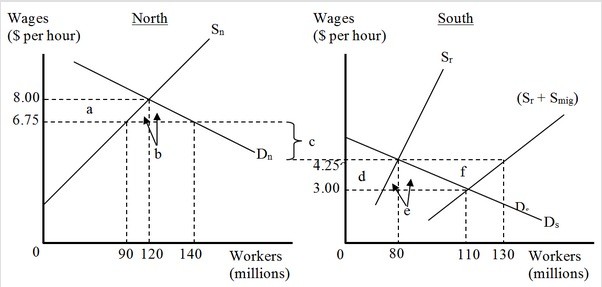 As an effect of the migration, the native employees in North
As an effect of the migration, the native employees in North
A. lose welfare given by area a. B. lose welfare given by area (a + b). C. gain welfare given by area (a + b). D. lose welfare given by area (e + f).
The classical model makes little distinction between the long run and short run because
A. current changes influence the long run, so it is not possible to plan for the future. B. wages and prices adjust so fast that the economy is quickly moving towards the long run. C. the model has not been fully developed yet. D. the classical economists knew that we are always operating in the short run.