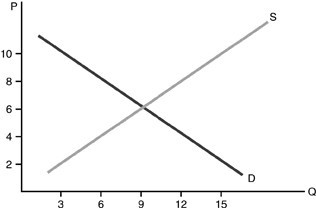
 Refer to the above figure. At a price of $2, excess quantity demanded equals
Refer to the above figure. At a price of $2, excess quantity demanded equals
A. 12.
B. 0.
C. 15.
D. 3.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Taking actions that reduce risk
A) raise your expected value. B) makes you less risk-averse. C) are impractical in most circumstances. D) change your utility function.
If Ripco owns the building where it operates, then if
a. the firm pays no rent, there is no opportunity cost b. the firm does not rent the building to anyone else, there is no opportunity cost c. the firm pays no rent, there is an opportunity cost d. its usage of the building precludes it from renting to anyone else, there is an opportunity cost e. the firm could use the building for other things, there is no opportunity cost
Assume that the central bank purchases government securities in the open market. If the nation has highly mobile international capital markets and a flexible exchange rate system, what happens to the quantity of real loanable funds per time period and reserve-related (central bank) transactions in the context of the Three-Sector-Model?
a. The quantity of real loanable funds per time period falls, and reserve-related (central bank) transactions remains the same. b. The quantity of real loanable funds per time period falls, and reserve-related (central bank) transactions become more negative (or less positive). c. The quantity of real loanable funds per time period rises, and reserve-related (central bank) transactions remains the same. d. There is not enough information to determine what happens to these two macroeconomic variables. e. The quantity of real loanable funds per time period and reserve-related (central bank) transactions remain the same.
As a firm increases the level of output that it produces, short-run average fixed cost
A. rises and then falls. B. decreases. C. decreases up to a particular level of output and then increases. D. remains constant since fixed costs are constant.