A mutation that changes a codon that originally coded for an amino acid into a stop codon is a
A) frameshift mutation.
B) missense mutation.
C) silent mutation.
D) nonsense mutation.
D) nonsense mutation.
A mutation that changes a codon that originally coded for an amino acid into a stop codon is a nonsense mutation.
You might also like to view...
Eukaryotes are ________.
A. often made of prokaryotic cells B. always multicellular C. often multicellular, sometimes unicellular D. always unicellular
Was their hypothesis supported by this experiment and why?
Bartel and Szostak hypothesized that among a large pool of RNA molecules, some of them may contain the enzymatic ability to catalyze a covalent bond between nucleotides; these can be selected for in the laboratory. The chart above shows the results from their experiment. The x-axis shows the original pool and 10 pools that were derived from their tagging of RNA with specific enzymatic functions; the y-axis shows the rate of phosphoester (covalent) bond formation.
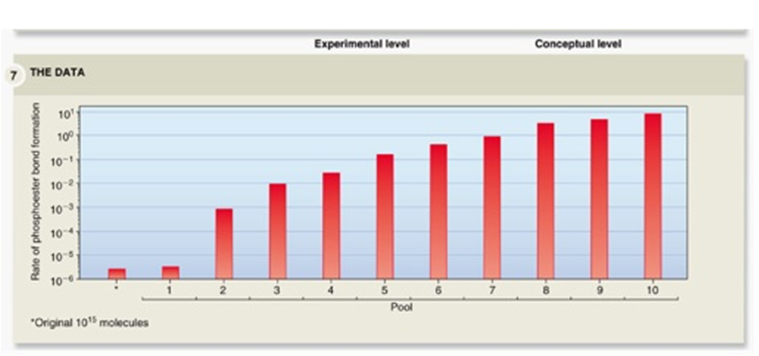
A. Yes, because pools 1 to 10 show a continual increase in covalent bond formation.
B. Yes, there is a definite increase from the original pool to the second pool, but not from pool 8-10.
C. No, because there is only a slight increase from the original pool to the first experimental pool.
D. No, because this figure does not give sufficient data to make that assumption.
Quaternary structure of a protein refers to ________
A) the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide B) alpha-helical or beta-sheet arrangements of protein structure C) three-dimensional coil of a polypeptide around itself D) the association of multiple polypeptide subunits to form a functional protein E) the number of amino acids in a polypeptide chain
Certain drugs use RNA interference as a mechanism of action. What molecule would the active compounds of these drugs be composed of?
A. protein B. small ion C. steroid D. nucleic acid E. carbohydrate