In rabbits, spotted coat (S) is dominant to solid color (s) and black (B) is dominant to brown (b). A true-breeding black spotted rabbit is mated to a true-breeding brown solid rabbit to produce a heterozygous F1 generation. Two F1 individuals are mated, and you do not see a 9:3:3:1 (black spotted: black solid: brown spotted: brown solid) ratio of offspring, but instead see that almost all offspring are a non-recombinant phenotype. This tells you that
A. that the genes for fur pattern (spotted vs. non-spotted) and fur color assort independently.
B. that the genes for fur pattern (spotted vs. non-spotted) and fur color are on the same chromosomes.
C. that the genes for fur pattern (spotted vs. non-spotted) and fur color are on different chromosomes.
D. that the genes for fur pattern (spotted vs. non-spotted) and fur color are epistatic.
E. that fur pattern (spotted vs. non-spotted) and fur color are maternally inherited.
B. that the genes for fur pattern (spotted vs. non-spotted) and fur color are on the same chromosomes.
You might also like to view...
The most abundant molecules in this structure are:a
structural proteins.
b. polysaccharides.
c. triacylglycerols.
d. phospholipid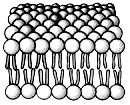
Lysosomes are responsible for ________
A) lipid synthesis B) cellular respiration C) digestion of organic matter inside the cell D) protein synthesis
Watson and Crick are credited with the discovery and description of the DNA
A) phosphate group. B) covalent bonds. C) double helix. D) deoxyribose sugar. E) hydrogen bonds.
Correctly match the definition and term: Replacement of hyaline cartilage with bony tissue to form a bone.
A. Interstitial growth B. Endochondral ossification C. Intramembranous ossification D. Epiphyseal plate E. Appositional growth