A chemical compound, regardless of its source (either natural or synthetic), that is capable of killing or inhibiting microorganisms is referred to as:
an antimicrobial
an antibiotic
a chemosynthetic agent
semisynthetic
an antimicrobial
You might also like to view...
There are more species in tropical areas than in places more distant from the equator. This is probably a result of _____
A) fewer predators B) more intense annual solar radiation C) more frequent ecological disturbances D) fewer agents of disease
The table shows the distribution of traits (A-E) in six extant species (1-6). A "0" indicates the ancestral condition, while "1" indicates the derived condition. Based on this data, which species would be considered the outgroup?
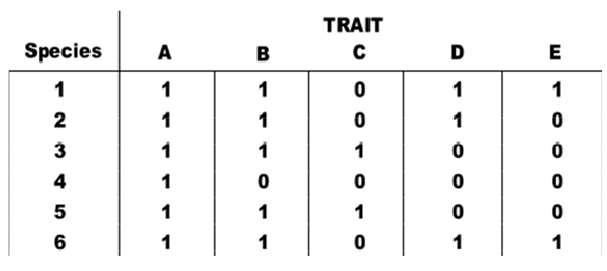
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
Clarify Question
· What is the key concept addressed by the question?
· What type of thinking is required?
· What key words does the question contain and what do they mean?
Gather Content
· What do you already know about cladistics?
Consider Possibilities
· What other information is related to the question? Which information is most useful?
Choose Answer
· Given what you now know, what information and/or problem solving approach is most likely to produce the correct answer?
Reflect on Process
· Did your problem-solving process lead you to the correct answer? If not, where did the process break down or lead you astray? How can you revise your approach to produce a more desirable result?
Which of the following microbial genera is used in the production of fermented dairy products?
A. Leuconostoc B. Streptococcus C. Lactobacillus D. All of the choices are correct.
Recombinant chromatids have a mix of paternal and maternal alleles due to
A. random fertilization of the gametes. B. crossing-over between the linked genes. C. persistent linkage of genes on the chromatid. D. independent assortment. E. point mutations and gene aberrations from replication.