Briefly explain the shape of the per-worker production curve in the Solow model. If investment per worker initially exceeds saving per worker, how is the steady-state capital—labor ratio achieved?
What will be an ideal response?
The per-worker production curve is positively sloped because adding capital to each unit of labor increases output per worker. The curve is concave (i.e., increasing at a decreasing rate) because of diminishing marginal productivity of capital; output increases at a slower rate than capital when capital is added to production.
The steady-state capital—labor ratio is the capital—labor ratio at which saving per worker [sf(k)] equals investment per worker [(n + d)k]. If investment per worker initially exceeds saving per worker, then the initial capital—labor ratio exceeds the steady-state capital—labor ratio. The capital—labor ratio will decline because saving is insufficient to provide enough capital to maintain the initial capital—labor ratio. The capital—labor ratio will continue to decline until it reaches the steady-state capital—labor ratio.
You might also like to view...
According to this Application, ________ regimes have difficulty coping with the changes arising from sustained technological progress
A) all political B) authoritarian C) participatory D) democratic
Using Figure 1 above, if the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD2 to AD3 the result in the short run would be: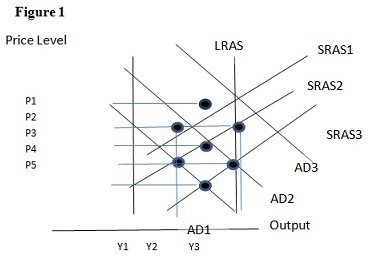
A. P1 and Y2. B. P2 and Y3. C. P3 and Y1. D. P2 and Y2.
One of the important conditions needed for economic growth is
a. rule of law. b. strong government. c. high average income. d. large government safety net.
Define open market operations and describe how the Federal Reserve Bank uses them to control the money supply.
What will be an ideal response?