The marginal benefit from a good is the amount a person is willing to pay for
A) all of the good the person consumes.
B) one more unit of the good.
C) all of the units of the good the person consumes divided by the number of units he or she purchases.
D) one more unit of the good divided by the number of units purchased.
B
You might also like to view...
Everything else being equal, a higher interest rate
a. increases consumption spending as people face increasing debt b. reduces consumption spending as people have a greater incentive to save c. does not change consumption spending because consumption is only affected by income d. does not change total consumption spending, but does change who does the spending e. reduces both consumption spending and saving as people face increased debt
The official poverty income threshold in the United States is
A. based on the cost of a budget that includes food, clothing, and shelter. B. never adjusted for the effects of inflation. C. the same for all families independent of the number of people in the family. D. calculated as three times the cost of a minimally acceptable diet for a family.
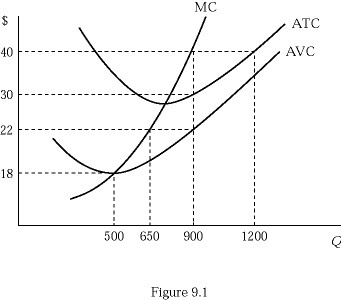 Figure 9.1 shows the cost structure of a firm in a perfectly competitive market. If the market price is $40 and the firm is currently producing the profit maximizing output level, its total variable cost is:
Figure 9.1 shows the cost structure of a firm in a perfectly competitive market. If the market price is $40 and the firm is currently producing the profit maximizing output level, its total variable cost is:
A. $12,500. B. $14,300. C. $19,800. D. $27,000.
In the United States, the wage floor legislated by government below which it is generally illegal to pay workers is known as
A. the wage ceiling. B. the going wage. C. the employment gap. D. the minimum wage.