Define the following terms and explain their importance to the study of economics.
a. monopolistic competition
b. oligopoly
c. cartel
d. oligopolistic interdependence
What will be an ideal response?
a. Monopolistic competition is a market structure in which products are differentiated, but which otherwise has the same characteristics as perfect competition. There are many industries in the United States, particularly in retailing, that are monopolistically competitive.b. An oligopoly is a market dominated by a few sellers, several of which are large enough relative to the total market to be able to influence the market price. Much of U.S. manufacturing is characterized by oligopoly.c. A cartel is a group of sellers of a product who have joined together to control its production, sale, and price in the hope of obtaining the advantages of monopoly. Cartels are illegal in the United States, but are often legal elsewhere. OPEC is a good example of a cartel.d. Oligopolistic interdependence is a fact in most oligopolies. Each oligopolist is influenced by decisions of its rivals; outcomes of its own decisions depend on the responses of rivals. The interdependence makes it very difficult to analyze oligopolistic behavior.
You might also like to view...
In the eighteenth century, the rise of manufacturing in New England helped the region attract more settlers than the other regions of the English colonies
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
If an industrial union is able to negotiate a wage above the market-clearing wage, employment in the industry will
a. increase b. decrease c. increase, if the union can restrict the supply of labor d. increase, if the union can increase the supply of labor e. decrease due to the strike-breaking activity of the firm
Are organizational changes always needed?
What will be an ideal response?
Refer to the information provided in Figure 2.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.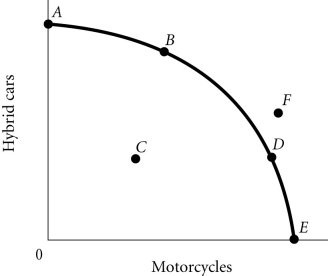 Figure 2.4According to Figure 2.4, Point A necessarily represents
Figure 2.4According to Figure 2.4, Point A necessarily represents
A. only hybrid cars being produced. B. an unattainable production point. C. what society wants. D. the economy's optimal production point.