Equal increases in government spending and taxes will:
a. cancel each other out so that the equilibrium level of real GDP will remain unchanged.
b. lead to an equal decrease in the equilibrium level of real GDP.
c. lead to an equal increase in the equilibrium level of real GDP.
d. lead to an increase in the equilibrium level of real GDP real GDP that is larger than the initial change in government spending and taxes.
e. lead to an increase in the equilibrium level of output that is smaller than the initial change in government spending and taxes.
c
You might also like to view...
In the simple circular flow model
A) businesses buy labor services from households, but supply other factors of production themselves. B) households spend their entire income on consumer products. C) profits are a type of income that is not received by households. D) households spend the income they receive from labor services but save the income they receive from selling the other factors of production.
Why does the opportunity cost of producing a good rise as more resources are devoted to producing that good?
What will be an ideal response?
Figure 18-2
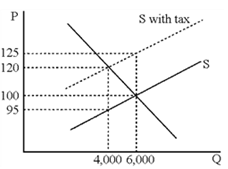
A. $5 B. $20 C. $25 D. $30
Macroeconomic always deals with ______ economy.
a. aggregate b. international c. personal d. government