An example of a sunk cost would be:
A. the price of a lift ticket you bought and used to ski the whole day.
B. the price of a lift ticket you bought and used for 1 run before you fell and broke your ankle.
C. the nonrefundable deposit you put on your vacation rental.
D. All of these are examples of sunk costs.
D. All of these are examples of sunk costs.
You might also like to view...
Which economic concept is illustrated by the saying "You can't have your cake and eat it too"?
a. Private property rights b. Economic freedom c. Scarcity d. Opportunity cost e. Gains from trade
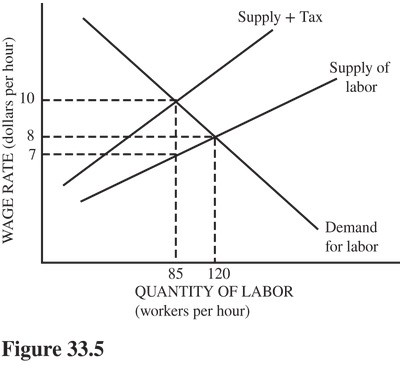 Refer to the labor market in Figure 33.5. Suppose the government imposes a payroll tax on employers. How much of the tax burden is passed on to workers?
Refer to the labor market in Figure 33.5. Suppose the government imposes a payroll tax on employers. How much of the tax burden is passed on to workers?
A. $8 - $7 = $1 per hour. B. $10 - $7 = $3 per hour. C. $7 per hour. D. $10 - $8 = $2 per hour.
Misperceptions theory helps explain what feature of the aggregate demand and aggregate supply model?
If the government imposes a sin tax on alcohol and the demand for alcohol is inelastic, the tax will cause a:
A. large decrease in quantity demanded but will generate more revenue than it would if the demand were elastic. B. large decrease in quantity demanded but will generate less revenue than it would if the demand were elastic. C. small decrease in quantity demanded but will generate less revenue than it would if the demand were elastic. D. small decrease in quantity demanded but will generate more revenue than it would if the demand were elastic.