It costs a firm $80 per unit to produce product A and $50 per unit to produce B individually. If the firm can produce both products together at $140 per unit of product A and B, this exhibits signs of
a. Economies of scale
b. Economies of Scope
c. Diseconomies of Scale
d. Diseconomies of Scope
d
You might also like to view...
If the reserve requirement on checkable deposits is .25, the ratio of currency held by the public to
demand deposits is .15, the ratio of time deposits to demand deposits is 3, the reserve requirement on time deposits is 0, and the ratio of excess reserves to demand deposits is 0, then the demand deposit multiplier is A) 5. B) 4. C) 3.33. D) 2.5.
A production or consumption quota that can be bought or sold is called:
A. a buyers' or sellers' quota. B. a tax. C. a tradable allowance. D. a subsidy.
In a theoretical sense, the "entrepreneurs" at a corporation are its
a. managers b. stockholders c. bondholders d. research and development staff e. boards of directors
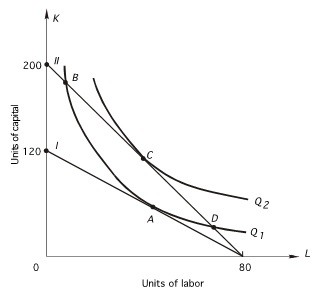 In the above graph, the shift from I to II was due to
In the above graph, the shift from I to II was due to
A. an increase in the price of labor. B. a decrease in the price of capital. C. a decrease in the price of labor. D. an increase in the price of capital. E. an increase in total cost.