The process by which financial institutions accept savings from businesses, households and governments and lend the savings to other businesses, households and governments is
A) asymmetric information.
B) adverse selection.
C) moral hazard.
D) financial intermediation.
D
You might also like to view...
"The Consumer Price Index increased by 4.2 percent in the first quarter of this year." What type of statement is this?
a. normative b. negative c. positive d. subjective e. biased
A "bad choice" as defined in choice architecture is a choice that:
A. policymakers consider not optimal for society, despite individual choosers' benefits. B. policymakers want to nudge participants away from. C. is considered not optimal by the choice architect. D. is one that the chooser will regret later.
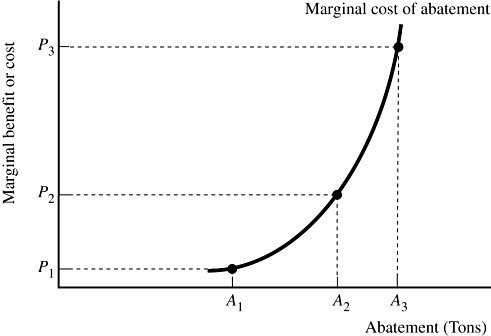 Figure 16.1A firm that generates pollution is illustrated in Figure 16.1. The government has chosen to impose a pollution tax equal to P2. From the firm's point of view, the marginal benefit of abatement is:
Figure 16.1A firm that generates pollution is illustrated in Figure 16.1. The government has chosen to impose a pollution tax equal to P2. From the firm's point of view, the marginal benefit of abatement is:
A. avoiding the pollution tax imposed by the government. B. the positive publicity the firm will receive by having a "green" production plant. C. the reciprocal of the marginal cost of abatement. D. zero because abatement benefits the general public, not the firm.
Without an accepted medium of exchange, people
A. have to specialize in one area of production. B. have to rely on barter in order to exchange goods and services. C. have to use credit to obtain goods and services. D. have to rely on gold or silver in order to exchange goods and services.