A runner runs 10 m from the origin toward the WEST to point A. He then runs from point A 20 m more toward the WEST to point B. He then runs from point B 30 m more toward the EAST to point C. The runner's total displacement from the origin to point C is
A. 60 m toward the WEST.
B. 50 m toward the EAST.
C. 20 m toward the WEST.
D. 10 m toward the EAST.
E. 0 m.
E. 0 m.
You might also like to view...
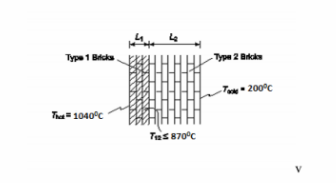
A furnace wall is to be constructed of brick having standard dimensions 22.5 cm* 11 cm * 7.5 cm. Two kinds of material are available. One has a maximum usable temperature of 1040°C and a thermal conductivity of 1.7 W/(m K), and the other has a maximum temperature limit of 8700C and a thermal conductivity of 0.85 W/(m K). The bricks have the same cost and are laid in any manner, but we wish to design the most economical wall for a furnace with a temperature of 10400C the hot side and 2000C on the cold side. If the maximum amount of heat transfer permissible is 950 W/m2 , determine the most economical arrangement using the available bricks.
GIVEN
Furnace wall made of 22.5 ? 11 ? 7.5 cm bricks of two types
Type 1 bricks Maximum useful temperature (T1,max) = 1040°C=1313 K
Thermal conductivity (k1) = 1.7 W/(m K)
Type 2 bricks Maximum useful temperature (T2,max) = 870°C= 1143 K
Thermal conductivity (k2) = 0.85 W/(m K)
Bricks cost the same
Wall hot side (Thot) = 1040°C=1313 K and cold side (Tcold) = 200°C=473 K
Maximum heat transfer permissible (qmax/A) = 950 W/m2
FIND
The most economical arrangement for the bricks
ASSUMPTIONS
One dimensional, steady state heat transfer conditions
Constant thermal conductivities
The contact resistance between the bricks is negligible
SKETCH
Monochromatic light (? = 500 nm) is incident on a soap bubble (n = 1.4) that is 500-nm thick. Calculate the change of phase of the light that penetrates the front surface, reflects from the second surface, and emerges through the first surface as an angle between 0° and 360°?
A. 280° B. 160° C. 220° D. 100° E. 290°
If you wish to send a beam of laser light from Earth to a space station above the atmosphere near the horizon, aim your laser
A) above your line of sight. B) below your line of sight. C) along your line of sight.
The number of electrons in an atom of an element is the same as the element's
a. atomic number. b. period number. c. mass number. d. group number.