An increase in productivity will cause which of the following according to the price-setting behavior of firms?
A) a reduction in prices set by firms
B) an increase in the real wage paid by firms
C) a reduction in the markup set by firms
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
D
You might also like to view...
Refer to Figure 3-6. The figure above represents the market for coffee grinders. Assume that the market price is $21. Which of the following statement is true?
A) There is a shortage that will cause the price to increase; quantity demanded will then decrease and quantity supplied will increase until the price equals $25. B) There is a shortage that will cause the price to increase; quantity supplied will then decrease and quantity demanded will increase until the price equals $25. C) There is a shortage that will cause the price to decrease; quantity demanded will then increase and quantity supplied will decrease until the price equals $25. D) There will be a shortage that will cause the price to increase; demand will then decrease and supply will increase until the price equals $25.
A person buys a bond with a face value of $10,000 for $9,195. Each year until the maturity date the bond buyer receives a coupon payment of $450 from the issuer of the bond. The coupon rate on the bond is
A. 4.9 percent. B. 4.5 percent. C. 7.0 percent. D. 6.75 percent.
Compare and explain the significance of the substitution and output effects as they apply to resource pricing. What relationship, if any, do they bear to the income and substitution effects discussed in connection with product demand?
What will be an ideal response?
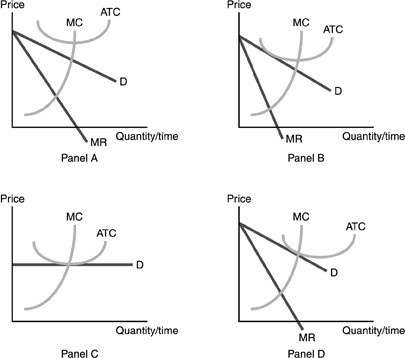 Refer to the above figure. Which panels represent long run equilibrium for the perfectly competitive firm and monopolistic competitive firm, respectively?
Refer to the above figure. Which panels represent long run equilibrium for the perfectly competitive firm and monopolistic competitive firm, respectively?
A. Panel C and Panel A B. Panel C and Panel D C. Panel C and Panel B D. Panel B and Panel C