In long-run equilibrium in a monopolistically competitive industry:
A. P > minimum ATC.
B. P < MC.
C. P = MC.
D. P = minimum ATC.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
A perfectly elastic demand curve has a price elasticity of demand coefficient of:
a. zero. b. 1. c. greater than 1, but less than infinity. d. less than 1, but greater than zero. e. infinity.
How do future expectations about the price of a good affect the present supply?
(A) If the price is expected to decrease, many producers will hold onto their supply. (B) If the price of a related good is expected to increase, only a few sellers will hold onto their supply until the increase occurs. (C) If the price is expected to increase, many producers will hold onto their supply. (D) If the price is expected to increase and then decrease, most sellers will hold onto their supply until the decrease has occurred.
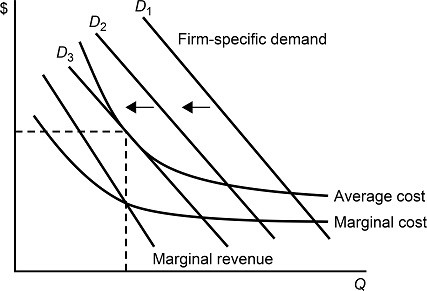
 Figure 8.3 shows demands and costs for a monopolistically competitive firm. When the firm's demand curve shifts from D1 to D2 and to D3, in the long run we would expect:
Figure 8.3 shows demands and costs for a monopolistically competitive firm. When the firm's demand curve shifts from D1 to D2 and to D3, in the long run we would expect:
A. the firm to earn a zero economic profit. B. the firm to charge a price equal to its marginal cost. C. the firm to increase its output level. D. the firm to produce at the lowest average cost.
The Mexican peso crisis of 1994 and 1995 was directly related to
A) a large capital account surplus. B) a large capital account deficit. C) an undervalued peso. D) a large current account surplus.