An electron is briefly accelerated in the direction shown in the figure below and to the left. It creates an EM wave pulse that eventually reaches points P and S 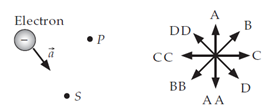 What is the direction of the wave’s motion at point P?
What is the direction of the wave’s motion at point P?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. Toward the viewer.
F. Away from the viewer.
T. The vector is zero.
G. AA
C. C
You might also like to view...
Briefly describe the two main lines of evidence for the modern theory of the moon's formation, wherein the Earth was hit by an approximately Mars-sized object
What will be an ideal response?
An observer moving with a light clock in a spaceship sees a light flash bouncing up and down between parallel mirrors in 1 nanosecond. An observer at rest outside the spaceship sees the same up-and-down flash in
A) 1 nanosecond also. B) less than 1 nanosecond. C) more than 1 nanosecond.
If the mass of the earth and all objects on it were suddenly doubled, but the size remained the same, the acceleration due to gravity at the surface would become
A) 4 times what it now is. B) 1/4 of what it now is. C) 2 times what it now is. D) the same as it now is. E) 1/2 of what it now is.
A 1.5-kg mass attached to an ideal massless spring with a spring constant of 20.0 N/m oscillates on a horizontal, frictionless track
At time t = 0.00 s, the mass is released from rest at x = 10.0 cm. (That is, the spring is stretched by 10.0 cm.) (a) Find the frequency of the oscillations. (b) Determine the maximum speed of the mass. At what point in the motion does the maximum speed occur? (c) What is the maximum acceleration of the mass? At what point in the motion does the maximum acceleration occur? (d) Determine the total energy of the oscillating system. (e) Express the displacement x as a function of time t.