In Figure 5.8, if the supply curve moves from S2 to S5,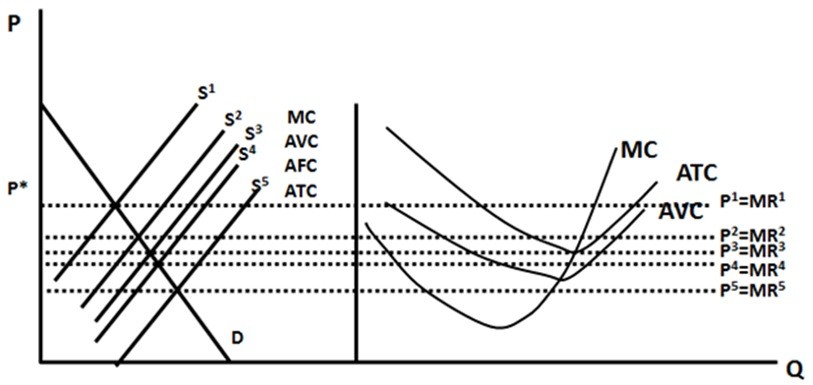 ,
,
A. the firm will go from making an economic profit to a loss but one that is not big enough to make it want to shutdown.
B. the firm will make a smaller economic profit than they used to.
C. the firm will go from making an economic profit to a normal profit.
D. the firm will go from making an economic profit to a loss that is big enough to make it want to shutdown.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
To aggregate 300 tons of steel, 5,000 bushels of wheat, and 1 million barrels of crude oil, economists add together the ________ of the three products
A. number of tons, bushels, and barrels B. units C. weight D. dollar value
For a consumer bound by the collateral constraint, a reduction in the price of the collateral leads to
A) nothing. B) an increase in current consumption and a decrease in future consumption. C) a decrease in current consumption and no change in future consumption. D) a decrease in current and future consumption.
Assume that the central bank purchases government securities in the open market. If the nation has low mobility international capital markets and a flexible exchange rate system, what happens to the real GDP and current international transactions in the context of the Three-Sector-Model?
a. Real GDP rises, and current international transactions become more positive (or less negative). b. Real GDP rises, and current international transactions become more negative (or less positive). c. Real GDP and current international transactions remain the same. d. Real GDP rises, and current international transactions remain the same. e. There is not enough information to determine what happens to these two macroeconomic variables.
Because of automatic stabilizers, when GDP fluctuates the...
What will be an ideal response?